The variety of flowering plants is amazingly large. To understand this diversity, botanists combine all types of plants into groups, which in turn are combined into larger groups. To establish such groups of plants, signs of their similarities and differences are used, by which one can judge the degree of relationship between plants.
Flowering plants have a more advanced structure than other groups. Only angiosperms produce flowers, and flowers produce pistils. The ovaries of the pistils contain the ovules. Flowering plants of different angiosperms differ in size, shape, color, and structure; The flowers of some angiosperms are adapted to pollination by wind, while others are adapted to pollination by insects. But with any method of pollination, pollen grains fall on the stigmas of the pistils, where pollen tubes are formed.
Pollen tubes with sperm grow to the ovules and grow into them, where fertilization occurs, which is characteristic only of flowering plants. In this case, an embryo is formed from the zygote resulting from the fusion of gametes. The most large cell after merging with the second sperm, it grows, divides, and an endosperm is formed, which stores nutrients for the embryo. Seeds develop from the ovules, and the pericarp develops from the wall of the ovary. 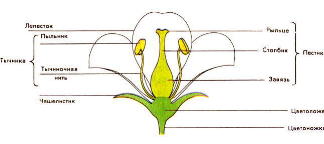
So, the seeds of flowering plants develop inside the fruit. That's why flowering plants called angiosperms. Currently, angiosperms dominate among the plants inhabiting the Earth's land.
Let's look at the plants blooming in autumn, For example, pansies, or tricolor violet. This plant, like most others, has organs:
roots and shoots. A shoot is a stem with leaves and buds located on it. Modified underground shoots are rhizomes, tubers and bulbs. Flowers can develop on the shoots. In their place, fruits with seeds ripen. Plants that bloom at least once in their life are called flowering plants.
The same organs of flowering plants can be very diverse in appearance.
A flower is a modified shoot, in the place of which a fruit with seeds or with one seed ripens.
Flower structure
Let's look at the structure of a flower. The flower develops on a peduncle that expands into the receptacle; All other parts of the flower are formed on it.
The brightly colored corolla consists of petals. Below the corolla there is a cup of green leaves - sepals. The corolla and calyx are the perianth that protects the internal parts of the flower from damage and can attract pollinating insects.
The main parts of a flower are the pistil and stamens. The stamen consists of a thin filament and an anther, which produces pollen. The pistil has a wide lower part - the ovary, a narrow style and a stigma. The fruit develops from the ovary. In some plants, other parts of the flower, such as the receptacle, also take part in the formation of the fruit. Only a few plants have flowers solitary. Most flowers are collected in inflorescences.
In summer and autumn, plants ripen in different shapes and colors.  fruits Fruits are formed from ovaries. The enlarged and modified walls of the ovary, which has become a fruit, are called the pericarp. There are seeds inside the fruit. Based on the number of seeds, fruits are divided into single-seeded and multi-seeded.
fruits Fruits are formed from ovaries. The enlarged and modified walls of the ovary, which has become a fruit, are called the pericarp. There are seeds inside the fruit. Based on the number of seeds, fruits are divided into single-seeded and multi-seeded.
There are juicy and dry fruits. Ripe juicy fruits have juicy pulp in the pericarp. Ripe dry fruits do not have pulp.
Plant seeds are distinguished by shape and size. The seed consists of a peel (hull), an embryo and contains a reserve nutrients. The embryo is divided into a germinal root, a stalk, a bud with leaves.
Plants that have one cotyledon in the seed embryo are called monocots.  In dicotyledonous plants, as the name suggests, the seed has two cotyledons. The supply of nutrients can be located in the cotyledons or in a special storage tissue - the endosperm. From the embryo of the seed, a new plant develops. A seed is the germ of a future plant.
In dicotyledonous plants, as the name suggests, the seed has two cotyledons. The supply of nutrients can be located in the cotyledons or in a special storage tissue - the endosperm. From the embryo of the seed, a new plant develops. A seed is the germ of a future plant.
Plants differ from each other in the color and shape of stems, leaves, flowers and fruits, life expectancy and other characteristics. But no matter how different flowering plants are, each of them can be classified into one of three groups: trees, shrubs and herbs.
Trees are usually large plants with perennial woody stems. Each tree has a trunk, branches, and tree branches form their crowns. Everyone is familiar with birch, aspen, linden, maple, and ash. Among the trees there are real giants, for example eucalyptus trees, reaching a height of more than 100 meters.
Shrubs differ from trees in that their trunk begins almost at the very surface of the soil and is difficult to recognize among the branches. Therefore, shrubs do not have one trunk, like trees, but several trunks extending from common ground. Shrubs are widespread: hazel, lilac, honeysuckle, elderberry.
Herbs, or herbaceous plants, usually have green, succulent stems; they are almost always lower than trees and bushes. But a banana, for example, reaches a height of 7 meters, and some hogweeds are taller than a person. There are tiny herbaceous plants. Duckweed lives on the surface of reservoirs; The size of each plant is several millimeters.
 Trees and shrubs - perennials. For example, some oak trees live for more than a thousand years. Among the herbs there are both perennial, annual and biennial.
Trees and shrubs - perennials. For example, some oak trees live for more than a thousand years. Among the herbs there are both perennial, annual and biennial.
Among the perennial herbs, lily of the valley, dandelion, coltsfoot, and nettle are well known. The aboveground parts of most of these herbaceous plants die off in autumn. In the spring, they develop anew, since these plants retain roots and other underground organs with buds in the soil under the snow.
Annual plants, such as violets, quinoa, gillyflower, radishes, buckwheat, oats, wheat, develop from seeds in the spring, bloom, form fruits with seeds and then die.
Biennial plants live for almost two years. In beets, radishes, and cabbage, only roots, stems and leaves usually develop in the first year. In the second year, these plants develop new shoots, bloom and produce fruits with seeds, and die off by autumn.
Article rating:
All-Russian Olympiad for schoolchildren
2015-2016 academic year
Biology, 11th grade
Tasks
Maximum score – 90,5
Part I You are offered test tasks requiring only one answer to be selected
out of four possible. Maximum amount points you can score – 30
(1 point for each test task). The answer index that you think is the most
complete and correct, please indicate in the answer matrix.
1. In flowering plants, the following develops from the wall of the ovary:
a) embryo;
b) seed coat;
c) endosperm;
d) pericarp.
2. Algae, which, thanks to their pigments, are most adapted to photosynthesis at great depths:
a) green;
b) red;
c) brown;
d) golden.
3. Functions of the root cap in plants:
a) ensuring root growth in length;
b) carrying water and solutions of mineral substances;
c) protection of the root apex from damage;
d) absorption of water and mineral solutions.
4. Name the type of fruit in potatoes:
a) tuber;
b) berry;
c) box;
d) achene.
5. Which plant has fibrous root system:
a) beets;
b) sunflower;
c) tulip;
d) peas.
6. Unisexual flowers are characteristic of:
a) pumpkins;
b) wheat;
c) peas;
d) rye.
7. What set of chromosomes is found in the endosperm cells of a wheat seed?
a) haploid; b) diploid; c) triploid; d) polyploid.
8. The inflorescence of the spike is characteristic of:
a) dill; b) plantain; c) lily of the valley; d) gladiolus.
9 Bacteria are pathogens:
a) scabies; b) hepatitis; c) cholera; d) malaria.
10. Which of the formations by origin is not a derivative of the skin epidermis:
a) whalebone; b) rhinoceros horn; c) pangolin scales; d) whiskers of a cat
a) bovine tapeworm; b) roundworm; c) pork tapeworm; d) echinococcus.
12. Which of the following organisms exhibits positive phototaxis:
a) chlorella; b) malarial plasmodium; c) euglena d) amoeba-proteus.
13. Insects with complete metamorphosis include:
a) Orthoptera, Diptera; b) hemipterans, homoptera; c) Coleoptera, Lepidoptera; d) Hymenoptera, dragonflies.
14. Roundworms differ from flatworms by the presence of:
A) nervous system; b) anus; c) cuticles; d) excretory system.
15. The figure shows the skeleton of a vertebrate animal.
In its structure one cannot find:
a) skull;
b) chest;
c) cervical vertebrae;
d) ribs.
16. Malaria is caused by:
a) amoebas; b) trypanosomes; c) plasmodia; d) ciliates.
17. The intestines are absent in:
a) liver fluke; b) wide tapeworm; c) pinworms; d) roundworms.
18. Human red blood cells are destroyed in:
a) thymus b) yellow bone marrow c) liver d) pancreas.
19. Of the listed enzymes, the following does not function in the small intestine:
a) chymotrypsin; b) lipase; c) pepsin; d) pancreatic amylase
20. Healing serum is:
a) antibody preparation b) weakened bacteria c) leukocyte suspension d) antibiotic solution.
21. Cartilaginous semirings form the basis of the skeleton:
a) trachea b) esophagus c) larynx d) bronchioles.
22. In the composition of the anterior roots spinal cord axons include:
a) conducting impulses from the brain b) motor neurons c) sensory neurons d) interneurons.
23. The unpaired bone of the skull is:
a) maxillary b) occipital c) parietal d) temporal.
24. The respiratory center in humans is located in:
a) cortex cerebral hemispheres b) diencephalon c) medulla oblongata d) cervical segments of the spinal cord.
25. Mucus covering the walls of the stomach:
a) inactivates salivary enzymes b) softens food c) promotes the conversion of pepsinogen into pepsin d) prevents self-digestion of the stomach walls.
26. The first stage of embryonic development is called:
a) neurula; b) blastula; c) crushing; d) gastrula.
27. Examples of homologous organs are:
a) dorsal fin of shark and dolphin;
b) digging limb of a mole and mole cricket;
c) pectoral fin of a perch and a human hand;
d) turtle shell and snail shell.
28. According to the results of genetic analysis, the wild ancestor of the domestic cat
are at least five representatives of one of the subspecies:

a) European cat;
b) forest cat;
c) jungle cat;
d) Chinese cat.
29. In ecosystems of great depths of the ocean there are necessarily:
a) animals, microorganisms; b) plants, microorganisms; c) plants, animals, microorganisms; d) plants, animals.
30. Interactions of individuals in a population, between populations are called:
a) abiotic factors; b) biotic factors; c) anthropogenic factors;
d) evolutionary factors.
31. The divergence of daughter chromatids to the poles occurs in meiosis in:
a) prophase I;
b) metaphase II;
c) anaphase I;
d) anaphase II.
32. What happens in an ecosystem if there are no decomposers in it or their activity is weakly expressed:
a) nothing happens;
b) accumulation occurs organic matter;
c) the number of producers decreases,
d) the number of consumers increases.
33. When crossing a ginger cat with a tortoiseshell cat, the offspring will be:
a) all kittens will be black;
b) half of the kittens will be red;
c) all cats will be red;
d) all cats will be black.
34. In the animal body, an oxygen molecule does not bind to:
a) myoglobin;
b) hemoglobin;
c) cytochrome c;
d) cytochrome a3.
35. Of the listed ecosystems, the lowest production per square meter have:
a) meadow;
b) taiga;
c) tropical forest;
d) open ocean.
Part II. You are offered test tasks with one answer option out of four possible, but requiring preliminary multiple choice. The maximum number of points that can be scored is 20 (2 points for each test task). The index of the answer that you consider to be the most complete and correct, indicate in the answer matrix.
1. Fungi and animals have similar characteristics:
1) the only posterior flagellum in motile cells;
2) autotrophic type of nutrition;
3) store glycogen;
4) ability for unlimited growth;
5) the presence of chitin.
a) 1, 2, 3;
b) 1, 2, 4;
c) 1, 3, 5;
d) 2, 3, 4;
e) 2, 3, 5.
2. The following compounds are involved in the regulation of blood sugar levels:
1) glucagon;
2) insulin;
3) prolactin;
4) testosterone;
5) estradiol.
a) only 1, 2;
b) only 1.5;
c) only 2, 3;
d) only 2, 4;
e) 1, 2, 3.
3. Plastic exchange processes include:
1) ATP synthesis;
2) photosynthesis;
3) protein synthesis;
4) glycolysis;
5) synthesis of nucleotides.
a) 1, 2, 3;
b) 2, 3, 4;
c) 2, 3, 5;
d) 2, 4, 5;
e) 3, 4, 5.
4. Indicators of biological regression are:
1) decreased life expectancy;
2) increase in embryonic mortality;
3) reduction species diversity;
4) decreased fertility;
5) reduction in size.
a) only 3;
b) only 1, 3;
c) only 1, 2, 3;
d) only 2, 3, 5;
e) 1, 2, 3, 4.
5. From the Central American center of origin (according to N.I. Vavilov)
are happening cultivated plants:
1) wheat;
2) corn;
3) rice;
4) soy;
5) sunflower.
a) only 1, 3;
b) only 1.5;
c) only 2.5;
d) only 1, 2, 5;
e) 2, 3, 5.
6. Distant hybridization in animals is difficult due to:
1) different set of genes in different types;
2) different sets of chromosomes in different species;
3) tissue incompatibility of different types;
4) different conditions species habitats;
5) different mating behavior of species.
a) only 1, 3;
b) only 1.5;
c) only 2.5;
d) only 1, 3, 4;
e) 2, 4, 5.
7. In eukaryotes, transcription occurs in:
1) core;
2) Golgi apparatus;
3) mitochondria;
4) plastids;
5) lysosomes.
a) 1, 2, 3;
b) 1, 2, 4;
c) 1, 2, 5;
d) 1, 3, 4;
e) 1, 3, 5.
8. One codon of messenger RNA can encode:
1) one amino acid;
2) two amino acids;
3) three amino acids
4) four amino acids;
5) not a single amino acid.
a) only 1, 2;
b) only 1, 3;
c) only 1, 4;
d) only 1.5;
e) 1, 2, 5.
9. Of the listed processes in mitochondria, the following occurs:
1) protein synthesis;
2) DNA synthesis;
3) synthesis fatty acids;
4) ATP synthesis;
5) oxidation of fatty acids.
a) only 3;
b) only 2, 4;
c) only 1, 3, 4;
d) only 1, 4, 5;
e) 1, 2, 4, 5.
10. Lipids are included in the composition :
1) ribosomes;
2) mitochondria;
3) chromatin;
4) nucleolus;
5) Golgi apparatus.
a) 1, 2;
b) 1, 5;
c) 2, 3;
d) 2, 4;
e) 2, 5.
Part 3. You are offered test tasks in the form of judgments, with each of which you must either agree or reject. In the answer matrix, indicate the answer option “yes” or “no”. The maximum number of points that can be scored is 20 (1 point for each test task).
1. The bulk of pine wood consists of vessels and mechanical fibers.
2. Photosynthetic products move through sieve tubes from top to bottom.
3. In a leaf vein, phloem is located at the bottom and xylem is at the top.
4. Oxygen is released by all green plants.
5. Plant roots can carry out photosynthesis.
6. The blood of a cockroach is colorless because it does not contain hemoglobin.
7. All ciliates have contractile vacuoles.
8. Kamchatka crab is a hermit crab, which is characterized by weak development of the abdominal region.
9. Lungfishes are an extinct group of fish from which land vertebrates evolved.
10. Characteristic feature of mammals is viviparity.
11. The main organ that, under the influence of the hormone insulin, ensures a decrease in the level of glucose in human blood is the liver.
12. Oxygen and carbon dioxide are transported in the blood only due to binding to hemoglobin and transfer as part of the hemoglobin-gas molecule complex.
13. The liver is capable of quickly and without serious consequences regenerating up to 70% of its volume removed during surgery.
14. The basis of biological membranes is a double layer of phospholipids.
15. The largest molecules in living organisms are muscle proteins.
16. The products of the dark stage of photosynthesis are glucose and oxygen.
17. Compounds essential for the human body include amino acids and nitrogenous bases.
18. In terrestrial ecosystems, the highest plant biomass densities are found in tropical forests.
19. The absence of intestines in tapeworms indicates the biological regression of this group of animals.
20. Mitochondria and lysosomes appeared in eukaryotic cells as a result of symbiosis.
Part 4. You are offered test tasks that require matching. The maximum number of points that can be scored is 15.5. Fill out the answer matrices in accordance with the requirements of the tasks.
( max . 3.5 points)
Here is a cross-section of a plant stem. Match the main structures of the conductive bundle (A-G) with their designations in the figure (1-7).

A – main parenchyma; B – sieve tubes; B – companion cells;
G – spiral vessel; D – sclerenchyma; E – porous vessel;
F – ringed vessel.
Designations
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Structures
2. ( max . 4 points)
The figure shows representatives of the fauna of the forest floor and upper soil horizons.


Establish a correspondence between organisms (1-8) and the taxa to which they belong (A–D): A) Centipedes; B) Arachnids; B) Protozoa; D) Crustaceans; D) Insects.
Organisms
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Taxa
3. ( max . 3 points)
Which of the listed structures are indicated in the figure by numbers 1 – 5?

A - bladder, B – kidney; B – kidney cortex; G – renal medulla; D – renal pelvis; E – ureter.
number
1
2
3
4
5
6
organ
4. ( max . 2.5 points)
For each product from the right column, find the corresponding substance from the left column.
A. Sucrose
1. Beef liver
B. Lipids
2. Beetroot
B. Lactose
3. Fish fat
G. Glycogen
4. Pea grains
D. Protein
5. Milk
1
2
3
4
5
5. ( max . 2.5 points)
Many species of arthropods are closely related to humans and their homes (1 – 5). Select from the list (A–D) the type of relationship that arises with the person.
1 – Housefly (Musca domestica)
2 – Bed bug(Cimex lectularius)
3 – Black(Blatta orientalis)And ginger(Blattella germanica)cockroaches
4 – Home spider(Tegenaria domestica)
5 – Mosquitoes sort ofCulex (urban form– C. pipiens f. molestus)
A) proto-cooperation
B) commensalism
B) neutralism
D) symbiosis
1
2
3
4
5
Member of the subject-methodological commission: /Skorykh S.A./
The ovary is the empty lower thickened part of the pistil - female organ plant propagation.
It provides protection and fertilization of the ovules (ovules) from which seeds are formed.
The pistil is located in the flower and consists of a stigma that traps pollen, a style that carries pollen inside, and an ovary where the seeds develop. After fertilization, a fetus is formed from it.
In the central part of the ovule (nucellus) there are eggs; in the case of pollination, they are fertilized and seeds develop from them. In the same place, an embryo sac is formed, from which they will feed.
Functions of the ovary
- Inside the ovary, the process of fertilization and seed maturation takes place;
- Protects ovules from external harmful environmental factors (temperature changes, drought, eating by insects, rain, etc.);
- Maintains the required level of moisture;
- Provides nutrition to seeds;
- It is the basis of the future fetus.

Types of ovary
According to the number of nests, that is, existing cavities separated by partitions in which the seeds are located, the ovary can be single- or multi-locular.

I - single-locular ovary, II - two-locular ovary, III - five-locular ovary. In all pictures: 1 - wall of the ovary; 2 - socket; a - ovules, 4 - seed carrier.
Another classification of ovaries is based on their location in relation to the receptacle.
The receptacle is the lower part of the flower, that is, its base, on which the petals, sepals, stamens and pistils are located.
According to the type of location, the ovary can be:
- Upper or free - located above the receptacle. It does not grow together with other parts of the flower; the flower is called subpistillate (cereals, ranunculaceae, legumes, etc.);
- The lower one is under the receptacle, the flower is attached to the top of the ovary, therefore it is called suprapistal (Asteraceae, cactaceae, orchids, etc.);
- Semi-inferior - grows together with the flower, but not at the very top; the flower is called semi-pistillate (saxifrage).

Formation of fruits from the ovary
 Fruits, depending on the type of formation from the ovary, are divided into several types: 1. Real - formed only by the ovary. Are divided into:
Fruits, depending on the type of formation from the ovary, are divided into several types: 1. Real - formed only by the ovary. Are divided into:
- Simple, formed by one pestle (cherry, plum, bird cherry, acacia bean);
- Complex, formed by several fused pistils (raspberries, blackberries)
- Fractional fruits are formed by a multilocular ovary with partitions (forget-me-not, basil, lavender, thyme, etc.);
2. False - formed with the participation of other parts of the flower such as the receptacle and perianth, including petals and sepals.

note
It is easy to distinguish false ones from real ones by the remains of parts of the flower (apples, pears).
Causes of damage to the ovary
Damage to the ovary can lead to a lack of further seeds and even fruits. The causes of damage may be:
- Late spring frosts during flowering, during which flowers and set fruits fall off. If the ovaries are partially damaged, then deformed, small, or unsuitable fruits develop from them;
- The absence or small number of pollinators, while some of the flowers remain unfertilized and are therefore discarded;
- Poor soil and lack of watering, when the plant does not have enough substances to grow all the ovaries that appear. In this case, it is necessary to add complex mineral and organic fertilizers and provide watering during drought;
- Pests (codling moth, apple sawfly, flower beetle, etc.). To get rid of them, you do not need to resort to artificial insect repellents, since they will also have a detrimental effect on pollinating insects. It is better to spray the plants with decoctions of herbs that repel pests (nettle, dandelion, garlic, wormwood, etc.)

- Leaf diseases. Healthy leaves are necessary to provide the plant with the necessary substances; without them, the ripening of fruits and seeds is impossible;

- Overload with the number of fruits: with large quantities formed ovaries, the plant cannot feed them all, so it discards some. Timely thinning of flowers will help to avoid this process.
Flowering plants are a large and diverse group that dominate most terrestrial ecosystems. Human existence depends on the main flowering plants cultivated by man. But for flowering plants to appear, they must go through the stage of pollination and fertilization. How this happens, read in this article.
Pollination
This process is carried out by the transfer of pollen from the stamens to the pistil. How does pollination and fertilization occur in flowering plants? This is done in two ways: self-pollination and cross-pollination. In the first case, the transfer of pollen grains to the pistil occurs in the same flower. This is how peas or tulips are pollinated. In cross-pollination, pollen from a flower from one plant is transferred to the pistil of another. most often by insects, in rare cases - by wind (sedge and birch), birds and water.
As a result of pollination by insects, bright, clearly visible flowers with pleasant smell and nectaries that produce a sweet liquid. These plants also produce a lot of pollen. It is food for insects. They are attracted by the bright colors or smell of flowers. When insects extract nectar, they touch the surface of the pollen grains, which stick to their body, and when they fly to a flower of another plant, they remain on the pistil. This is how pollination by insects occurs. Many are pollinated only by certain insects: fragrant tobacco - night butterfly, creeping clover - by a bee, and meadow clover - by a bumblebee.
Cross-pollinated plants are better able to cope with changing conditions environment. But the pollination process in this case depends on a number of factors. And self-pollination does not depend on anything. He is not afraid of weather conditions and the absence of intermediaries.
Fertilization
The pollen grain, falling on the stigma of the pistil, begins to gradually germinate. From the vegetative cell, a long pollen tube develops. Growing up, it reaches the level of the ovary, and then the ovule. At the same time, a pair of sperm is formed, which penetrates the pollen tube. She, in turn, enters the ovule through the pollen passage. Then the tube at the very tip ruptures and releases the male sperm, which are immediately sent to the embryonic membrane, called the sac. This is where the eggs develop.

Next, the egg is fertilized by one sperm and a zygote is formed, from which a small embryo of a completely new organism of plant origin begins to form. At the same time, the second sperm merges with the zygote nucleus or with the polar nuclei. As a result, a triploid cell is formed, from which the endosperm arises. It is called nutrient tissue, which contains reserves of necessary substances for normal development embryo of the future plant. This is how the reproductive organs of flowering plants are represented.
When one sperm with an egg, and the other with polar nuclei, merge together, this process is called. It is characteristic only of flowering plants and is unique feature angiosperms. The fertilized ovule grows into a seed. As a result, the ovary of the pistil grows. In flowering plants, the fruit develops from the wall of the ovary.
Reproduction
Any plant, having reached a certain size and having gone through the appropriate stages of development, begins to reproduce organisms of a similar species. This is reproduction, which is necessary property life. All organisms thus prolong the existence of the species itself. There are sexual and those that occur with the participation of one individual. When plants develop specialized cells called spores, the organisms begin to reproduce.

Mosses, algae, ferns, mosses and horsetails. Spores are special small cells with a nucleus and cytoplasm that are covered with a membrane. They are able to withstand poor conditions for a long time. But when they find themselves in a favorable environment, they quickly germinate and begin to form daughter plants, whose properties do not differ from those of the mother.
During sexual reproduction, female and male reproductive cells merge, resulting in the formation of daughter organisms that are qualitatively different from the parent ones. Parental organisms of the feminine and masculine principles are already taking part here.
The macrosporangium plays a dominant role in the composition of the ovule. It is in it that the laying of one mother cell occurs, from which macrospores are formed. The three pieces begin to die off and eventually collapse. Fourth macrospore - feminine, lengthens and its core divides. Then the daughter nuclei move to different poles of the elongated cell. Each nucleus formed further divides twice.

Cells located near different poles form four nuclei. This is called the embryo sac, which contains eight haploid nuclei. Then, from each four nuclei, one of them moves to the center of the embryo sac. There they merge, as a result of which they form a secondary nucleus - diploid.
Then, in the embryo sac, in the cytoplasm, partitions are formed between the nuclei at the cellular level. The bag becomes seven cells. Near one of its poles is the egg apparatus, which includes a large egg and two auxiliary cells. At the other pole there are antipodal cells, there are three in total. So, there are now six in the bag and one is diploid, with a secondary nucleus. It is located in the center of the embryo sac.
What is an ovary?
It is called the lower thickened part of the pistil with a cavity closed inside in which the ovules are located. Pollen falls from the stigma of the pistil into the ovule, which is protected from unfavorable conditions by an internal moist cavity. In the ovule, the development of female germ cells - eggs - occurs.

What types of ovaries are there?
The types of ovaries of flowering plants are:
- Upper. It is attached to the receptacle freely, without merging with other parts of the flower. The walls of the ovary are formed from carpels. In flowering plants, the fruit develops from the wall of the ovary. Examples are buttercups and cereal plants. These flowers are called subpistillate or circumpistillate.
- The inferior ovary is always located under the receptacle. It is formed with the participation of other parts of the flower: the base of the sepals and stamens with petals, which in many flowers are attached to the top of the ovary. In flowering plants, a fruit develops from the wall of the ovary. Examples are Asteraceae, cactus and orchid plants. The flower is called suprapistal.

- Semiinferior ovary. Its top does not grow together with other parts, so it is free. Flowers of this type are called semi-supristal. These are the types of ovaries of flowering plants.
Flowering plants
They are the most progressive group of plants, numbering two hundred and fifty thousand species, distributed throughout planet Earth. The smallest plant is duckweed, with a diameter of one millimeter. She lives in the water. The largest flowering plants are trees, reaching a height of one hundred meters or more.

The appearance of flowering plants occurs due to the development of a special reproductive organ - the flower. In some plants it is colored bright colors, others smell wonderful. The flowers are small and inconspicuous in plants that look like grass. Despite the huge variety of flowering plants, they all fit harmoniously into our lives: they decorate gardens and parks, and give us the joy of communicating with them.
Flower structure
The flower is complex system organs that ensure the propagation of plants by seeds. Its appearance led to the widespread distribution of angiosperms (flowering) plants on Earth. The flower has many functions. With its participation, stamens with pollen grains and pistils with ovules are formed. He plays main role in pollination, fertilization, formation of seeds and fruits.
The flower is a shortened, modified shoot of limited growth, bearing a perianth, pistils and stamens. All have flowers similar in structure and different in shape. This is how adaptation to pollination occurs in various ways.
The flower may end on the main or lateral stems, the bare part of which under the flower itself is called the peduncle. It is greatly shortened or completely absent in sessile flowers. The peduncle turns into a receptacle, which can be elongated, convex, concave or flat. All parts of the flower are placed on it. These are sepals with petals, stamens with a pistil, in the lower part of which the ovary is formed, which contains the ovules or ovules. A flower with such an ovary has a concave receptacle. If the ovary forms at the top of the pistil, the receptacle will be convex or flat.




