According to statistics, over 70% of all residential buildings are heated using water heating. One of its varieties is a two-pipe heating system - this publication is dedicated to it.
The article discusses the advantages and disadvantages, diagrams, drawings and recommendations for installing two-pipe wiring with your own hands.
Contents of the article
Differences between a two-pipe heating system and a single-pipe one
Any heating system is a closed circuit through which coolant circulates. However, unlike a one-pipe network, where water is supplied to all radiators in turn through the same pipe, a two-pipe system involves dividing the wiring into two lines - supply and return.
A two-pipe heating system for a private house, in comparison with a single-pipe configuration, has the following advantages:
- Minimal coolant losses. In a single-pipe system, radiators are alternately connected to the supply line, as a result of which the coolant passing through the battery loses temperature and enters the next radiator partially cooled. With two-pipe configuration, each battery is connected to the supply pipe with a separate outlet. You get the opportunity to install on each of the radiators, which will allow you to regulate the temperature in different rooms houses independently of each other.
- Low hydraulic losses. When arranging a system with forced circulation(necessary in large buildings) a two-pipe system requires the installation of a less efficient circulation pump, which allows for significant savings.
- Versatility. A two-pipe heating system can be used in multi-apartment, single or two-story building.
- Maintainability. On each branch of the supply pipeline it is possible to install shut-off valves, which makes it possible to cut off the coolant supply and repair damaged pipes or radiators without stopping the entire system.

Among the disadvantages of this configuration, we note a twofold increase in the length of the pipes used, however, this does not threaten a dramatic increase in financial costs, since the diameter of the pipes and fittings used is smaller than when installing single pipe system.
Classification of two-pipe heating
The two-pipe heating system of a private house, depending on its spatial location, is classified into vertical and horizontal. The more common is the horizontal configuration, which involves connecting radiators on a building floor to a single riser, while in vertical systems radiators from different floors are connected to the riser.
The use of vertical systems is justified in a two-story building. Despite the fact that such a configuration is more expensive due to the need to use more pipes, with vertically located risers, the possibility of air pockets forming inside the radiators is eliminated, which increases the reliability of the system as a whole.

Also, a two-pipe heating system is classified according to the direction of movement of the coolant, according to which it can be direct-flow or dead-end. In dead-end systems, liquid circulates through the return and supply pipes in different directions; in direct-flow systems, their movement coincides.
Depending on the method of transporting the coolant, systems are divided into:
- with natural circulation;
- with forced circulation.
Heating with natural circulation can be used in one-story buildings with up to 150 square meters. It does not provide for the installation of additional pumps - the coolant moves due to its own density. Characteristic feature systems with natural circulation is to lay pipes at an angle to horizontal plane. Their advantage is independence from the availability of power supply, the disadvantage is the inability to adjust the water supply speed.
In a two-story building, a two-pipe heating system is always performed with forced circulation. In terms of efficiency, this configuration is more effective, since you get the opportunity to regulate the flow and speed of the coolant using circulation pump, which is installed on the supply pipe leaving the boiler. In heating with forced circulation, pipes of relatively small diameters (up to 20 mm) are used, which are laid without a slope.
Which heating network layout to choose?
Depending on the location of the supply pipe two-pipe heating classified into two types - with upper and lower wiring.
The diagram of a two-pipe heating system with top wiring involves installing an expansion tank and a distribution line at the highest point of the heating circuit, above the radiators. This installation cannot be done in one-story building With flat roof, since to place communications you will need an insulated attic or a specially designated room on the second floor of a two-story house.

A two-pipe heating system with bottom wiring differs from the top one in that the distribution pipeline in it is located in the basement or in an underground niche, under the radiators. The outermost heating circuit is the return pipe, which is installed 20-30 cm lower than the supply line.
It's more complex configuration, requiring the connection of an upper air pipe through which excess air will be removed from the radiators. With absence basement additional problems may arise due to the need to install the boiler below the level of the radiators.

Both the lower and upper circuits of a two-pipe heating system can be made in a horizontal or vertical configuration. However, vertical networks, as a rule, are made with bottom wiring. With this installation, there is no need to install a powerful pump for forced circulation, since due to the difference between the temperatures in the return and supply pipes, a strong pressure drop is created, increasing the speed of movement of the coolant. If, due to the specific layout of the building, such installation cannot be done, a main line with overhead routing is installed.
Making a two-pipe system with your own hands (video)
Selecting pipe diameters and rules for installing a two-pipe network
When installing two-pipe heating, it is extremely important to choose the correct pipe diameter, otherwise you may get uneven heating of radiators located far from the boiler. Most boilers for domestic use have a diameter of the supply and return pipes of 25 or 32 mm, which is suitable for a two-pipe configuration. If you have a boiler with 20 mm pipes, it is better to opt for a single-pipe heating system.
Size chart available on the market polymer pipes consists of diameters 16, 20, 25 and 32 mm. When installing the system yourself, you need to take into account the key rule: the first section of the distribution pipe must match the diameter of the boiler pipes, and each subsequent pipe section after the branch tee to the radiator is one size smaller.

In practice, it looks like this: a diameter of 32 mm comes out of the boiler, a radiator is connected to it through a tee with a 16 mm pipe, then after the tee the diameter of the supply line is reduced to 25 mm, at the next branch to the radiator line 16 mm after the tee the diameter is reduced to 20 mm and so on. If the number of radiators is greater than the standard sizes of pipes, it is necessary to divide the supply line into two arms.
When installing the system yourself, adhere to the following recommendations:
- the supply and return lines must be parallel to each other;
- each outlet to the radiator must be equipped with a shut-off valve;
- distribution tank, if installed in attic when installing a network with top wiring, it is necessary to insulate it;
- pipe fastenings on the walls should be placed in increments of no more than 60 cm.
When setting up a system with forced circulation, it is important to correctly select the power of the circulation pump. The specific choice is made based on the size of the building:
- for houses with an area of up to 250 m2, a pump with a capacity of 3.5 m3 / hour and a pressure of 0.4 MPa is sufficient;
- 250-350 m2 – power from 4.5 m3/hour, pressure 0.6 MPa;
- over 350 m 2 - power from 11 m 3 / hour, pressure from 0.8 MPa.
Despite the fact that it is more difficult to install two-pipe heating with your own hands than a one-pipe network, such a system, due to its high reliability and efficiency, fully justifies itself during operation.
The two-pipe system is the most popular scheme for a water heating complex. The scheme compares favorably with maneuverability and ease of regulation from a single-pipe system, and is more economical in the amount of material compared to the manifold configuration. The publication material gives an overview of the structure and principle of operation, the types of two-pipe configuration of the heating complex.
Construction of a two-pipe heating system
Diagram of a two-pipe water heating systemIn water heating, pipelines are one of the main elements; they serve to supply heated coolant liquid to heating devices and return the water that has given off heat to the heat source. When autonomous heating The heat source is an individual boiler; in the case of central heating, main pipelines.
To ensure the circulation of coolant between radiators and the heat source in water heating, 3 main schemes are used:
- Single-pipe;
- Two-pipe;
- Collector (radial).
In addition, these schemes are sometimes combined with each other. The disadvantage of a single-pipe scheme is the difficulty of controlling and adjusting the temperature in individual rooms and heating devices. The collector system requires the largest amount of material for installation compared to other types of systems.
The two-pipe scheme is the “golden mean” and is the most popular, especially during the construction autonomous systems heating. The popularity of this type of system is due to the ease of regulation due to the hydraulic content of the circuit.
The basic principle of a two-pipe system is based on parallel connection heating devices to two independent pipelines. One of them serves to supply hot coolant to heating devices (radiators, convectors, registers, etc.), the second - to return the cooled coolant to the boiler for heating.
Direct and return pipelines act as collectors, the water pressure along the length changes slightly. This allows you to maintain approximately the same pressure at all points of the heating system.
Equal pressure in all heating devices makes it easy to regulate the temperature on individual devices in rooms. Installation of thermostatic fittings, thermal heads, temperature sensors makes it possible to fully automate the temperature control process.
Maintaining the same hydraulic characteristics is also carried out by changing the diameter of the pipes along their length - in the dead-end branches of the system. The flow area decreases gradually from the first to the last radiator - this configuration of a two-pipe circuit is called a dead-end configuration. In addition to it, there is another type of scheme - associated (or Tichelman loop).
Types of two-pipe heating system
 Main types of two-pipe heating circuit
Main types of two-pipe heating circuit The dead-end design of a two-pipe system is more popular than the Tichelman loop. Its construction usually requires less material.
As stated above, the basic principle of constructing a dead-end system is a gradual reduction in the diameters of the direct and return pipelines along the length of the branch, from the first to the last heating device.
Temperature regulation is carried out by control valves. It is worth noting that when installing any type of water heating system, shut-off and control valves should be installed on each heating element. This is necessary to turn off the radiator or other heating device for prevention (flushing) or repair. When any device in a two-pipe network is turned off, the system continues to work - this is a significant advantage of the described scheme.
The adjustment algorithm is as follows. On the first radiator, the control valves are closed as much as possible, leaving a small coolant flow. On each subsequent device, the valve (or tap) is opened a little more. This stepwise adjustment allows you to equalize the pressure along the length of the circuit and adjust the required coolant flow rates (and, accordingly, the temperature).
A small disadvantage of the dead-end construction of a two-pipe circuit is that if the control valves on the first or second radiator are significantly opened, they can operate in bypass mode. This situation occurs rarely and is usually caused by incorrect selection of pipeline diameters.
More favorable in hydraulic terms is the associated scheme, also known as the Tichelman loop. Here, the forward and return pipelines have the same diameter and are connected to the radiators from different directions. This allows you to practically equalize the coolant pressure in all heating devices without major adjustments by control devices - valves or taps.
The installation of a line according to the Tichelman scheme requires more pipeline than the assembly of a dead-end branch. The use of one or another scheme is usually justified by the construction parameters of the heated building - dimensions and relative position premises.
A two-pipe system allows you to install more radiators on one line than a single-pipe analogue. Moreover, the Tichelman loop can work efficiently with a large number heating elements than a dead-end configuration due to its hydraulic structure.
Two main types of two-pipe systems - dead-end and associated - serve as the basic elements. The general structure of the entire heating complex has the following Constructive decisions:
- Connecting system branches to vertical risers for more than 1 floor;
- Insertion of system branches into horizontal planks placed in the lower or upper part of the building;
- Connecting dead-end branches or associated schemes Tichelman to distribution manifolds;
- Construction of a two-pipe system with natural circulation.
A prerequisite for connecting dead-end or associated branches to risers and sunbeds is the installation of balancing valves at the connection point. They are necessary for the general hydraulic adjustment of the entire heating system.
It is worth noting that the two-pipe scheme is used mainly in closed systems with forced circulation. Construction open system with natural circulation most often requires balancing - installation of shut-off and control valves.
 Scheme of a two-pipe system with natural coolant circulation
Scheme of a two-pipe system with natural coolant circulation For the presented scheme it is mandatory technical solution a tap will be installed and the flow to the first radiator will be limited, otherwise the coolant will flow along the shortest path. In this case, subsequent radiators will receive insufficient heat.
Installing a tap or valve that has a certain hydraulic resistance may introduce an imbalance in gravitational movement coolant. Therefore, the best solution for organizing natural circulation is a single-pipe scheme, usually performed in this case without bypasses.
The two-pipe heating system is the most popular configuration of water radiator heating of premises. Thanks to its advantages - maneuverability, ease of balancing, independence of instruments - it rightfully occupies a leading position in design solutions heating complexes.
In apartments and private houses, an integral part of comfort is the provision of heat. Water heating is predominantly used. Water heating Available with one-pipe and two-pipe circuits. In the first case, the water, passing through a closed circuit, cools down greatly. Each subsequent radiator receives colder liquid. The two-pipe system eliminates this disadvantage.
A two-pipe heating system is effective for a private home. These designs have become more popular. The complexity of installation and slightly higher consumption of materials pay off with clear advantages.

Advantages of two-pipe heating:
- Each radiator receives equally heated coolant, increasing the air temperature in the room.
- Possibility to regulate the heat of each battery by setting a thermostat.
- If one of the systems breaks down, repairs can be carried out without stopping the heating. To do this, it is necessary to install locking elements.
- For installation, you can use pipes of small diameter, significantly saving money.
- Installation in a room of any size.
A distinctive feature of the system is the connection of 2 pipes to each radiator. Through the first, heat enters the battery, the second removes cooled liquid from the device. This design allows you to efficiently heat the room.
Layout of pipes for a two-pipe heating system
There are two types of two-pipe wiring: vertical and horizontal. In the first case, the heating elements are located vertically along one riser, which is typical for apartment buildings. In most cases, the coolant is supplied upward, and the outlet flows downwards by gravity.
At horizontal version, the batteries are located in one line. This layout is typical for one-story buildings.
The two-pipe design can be in open or. Any heating includes elements expansion tank. When heated, the pressure in the pipes increases, and the compensation system allows you to maintain the required operating level. The device is located at the highest point, usually in the attics of houses. When the wiring is open, the liquid in the tank comes into contact with air. Part of it evaporates, so such a system requires constant monitoring. IN closed type, the design is equipped with a membrane and does not require constant attention.

Advantage of the scheme:
- More aesthetic appearance premises, pipes are hidden under radiators and are not noticeable;
- To pass to the radiators, one hole is required;
- Heat losses are reduced.
All heating systems can be made with natural and forced circulation. The choice of design is influenced by the upper or lower water supply. For bottom supply, forced water circulation must be installed. Pipes from the boiler to the radiators are laid at floor level, just below the radiators. There are 2 pipes running along the entire perimeter of the room: distribution and return. They are connected to each radiator using fittings and tees. Such a system can be constructed from metal-plastic or polypropylene pipes independently, without resorting to the services of specialists.
Option with top wiring in a two-pipe heating system of a private house
In private homes, you can install both lower and upper distribution. For overhead distribution, it is preferable to use natural water circulation. The distribution with hot coolant is pulled from the boiler to the ceiling, then laid around the perimeter of the building.
Description of design:
- From the top pipe, bends are lowered vertically to the radiators;
- The reverse course is laid according to the floor level;
- Connect both pipes to the radiators;
- For physical circulation, the angle of inclination of the pipe should be 3-5ᵒ, while the compensation tank is installed at the highest point of the diagram.

The natural circulation heating system starts working when the water is heated. The coolant becomes lighter and rushes upward, reaching the highest point of the circuit, then goes down through the pipes into the radiators, cools down and becomes heavier, and goes back into the boiler.
The lower the room temperature, the faster the water circulation in the batteries.
The maximum effect from the top distribution can be obtained in 2 storey building. Natural circulation will be stimulated by the difference in height of the radiators on the 2nd floor and by installing the boiler in the basement. The disadvantage of the upper circuit is the external aesthetic appearance; in addition, part of the heat goes up. You can compensate for the deficiency by combining single-pipe and two-pipe heating. For example, make a single-pipe heated floor on the 2nd floor, and install a two-pipe installation on the 1st floor.
Accurate calculation of a two-pipe heating system
Before starting work, it is necessary to draw up a heating scheme, decide on the material, and make a hydraulic calculation. It is necessary to calculate the pressure drop in the rear section or to calculate the diameter of the pipe.
The calculation is carried out taking into account the following factors:
- Inner surface of pipes and its roughness;
- Section diameter;
- Number of pipe bends;
- Pressure difference between supply and return;
- Number of radiators and their cross-section;
- Locking elements.

When making calculations, use formulas and an axonometric table. You can use a special software program. The most loaded ring or contour is taken as the main object. As a result of calculations, the optimal speed of movement should be from 0.3 to 0.7 m/s.
At a higher speed, the heating will make noise; at a lower speed, a strong temperature variation will occur.
After the calculations have been carried out, pipes of effective diameter are purchased, required amount radiators, boiler, fittings, pipes, expansion tank, circulation pump, if necessary.
Stages of work on installing two-pipe heating with your own hands
Installation of a heating system begins with the installation of a boiler. The heat generator using gas and electricity is located in any room. For liquid and solid fuel boilers, a separate niche is required. When installing radiators, it is necessary to take into account a pipeline slope of 1-2% in relation to the entire length of the pipe.
Work plan:
- Boiler installation.
- The main pipe with hot water, running through all radiators.
- Parallel to the first, a second highway is laid in reverse.
- With a forced heating option, a circular pump is installed.
- Radiators are installed. The batteries are suspended on special brackets. All radiators must be located at the same level. For ease of use, they are equipped with shut-off valves at the entry and exit points. Batteries are connected in several ways: side, diagonal, bottom connection. The most effective lateral and diagonal designs.
- The heating system is completed by installing pipes of associated components, installing an expansion barrel and additional elements.

The line should not contain right or sharp corners, as the resistance will increase. Taps and valves must match the size of the pipes. In a design with top wiring, the expansion tank is placed in an insulated attic. After all installation work is completed, it is time to connect the system.
To do this, turn off all the taps and be sure to slowly fill the supply circuit.
Next, open the valve of the first battery and bleed the air until a smooth stream comes out. The element is closed and the radiator outlet valve is opened. These manipulations must be carried out with each radiator. All detected defects are eliminated.
Do-it-yourself two-pipe heating of a private house (video)
Installing a two-pipe system with your own hands will take more time, ultimately provide effective and practical heating, and will save on installation work. It is important to choose the right option for your home and make a competent calculation of the system parameters. Skillful hands and following the instructions will transform the house, making it cozy and warm.
Examples of heating wiring in a private house (photo)


















The heating system of a private house is a mandatory and integral part of housing in the Russian Federation, the territory of which is located mainly in cold climatic zone. Regardless of the type of heat generator (gas, electric, solid and liquid fuel boilers) heat sources (radiators, registers or batteries) are installed in the house, and the two-pipe heating system circuit is currently the most popular and preferred because of its efficiency and high efficiency. Although the single-pipe scheme is simpler and cheaper to install, it is less effective, since it does not have the ability to regulate heat transfer in each room and for each heating device, be it a battery, a radiator or a homemade pipe register.
Types of double-circuit coolant distribution
The main advantage that the two-pipe heating scheme gives is the very high efficiency heat transfer, so even double the cost of pipes, in comparison with a single-pipe network, is justified many times over. What explains this? Pipes in this scheme are used with a small diameter - the main source of heat is the radiator - and due to significant savings on materials, it is possible to reduce the cost estimate. You also need to purchase much fewer fittings, valves and other accessories. The entire system assembly is easy to do yourself. 
Equipment in a private house for two-pipe heating means warmth, coziness, comfort and quality of the heating method used. The arrangement itself two-pipe scheme- this is the supply of two pipes to each radiator: one is supplied with hot coolant, the second is discharged. The supply is connected to all radiators in parallel, and a shut-off valve is installed in front of each heat source to regulate heat exchange, carry out preventive maintenance or repair the system without a general shutdown.
To install pipework using a two-pipe scheme, you will need to purchase the following materials:
- Heating boiler, expansion tank and a circulation pump (if it is not already installed in the boiler);
- Heating radiators or batteries, safety valve, pressure gauge;
- Purification reagents, accessories (quantity and functionality are determined based on the project or diagram), air exhaust devices (Mayevsky taps, valves);
- Metal-plastic or PVC pipes.
And these tools:
- Impact type electric drill and screwdriver;
- Welding machine and electrodes with a diameter of 3-4 mm;
- Keys – adjustable and gas, as well as a tape measure and a hammer;
- Plumb and spirit level.

Essential and fundamental difference between heating schemes in the vertical and horizontal planes lies in their wiring. The pipes enclose all the batteries in one system, but in different patterns.
Heating with wiring on top - varieties
Home heating systems with overhead wiring connect all radiators to a vertical riser that supplies heated coolant to the system. This is a reliable system in operation, since air plugs cannot appear in it, but installation and wiring are more expensive than a single-pipe circuit. This heating scheme is optimal for a low-rise house or cottage, since each floor can be connected to the boiler with a separate branch.
A two-pipe horizontal connection is relevant for one-story house. Heat sources are connected to horizontally separated pipes, the risers of which are usually installed in hallways, halls or corridors. 
Such a two-pipe heating system, the circuit of which is assembled according to the horizontal type, can have radial (collector) and sequential types of radiator connections. With radiant wiring, the coolant is supplied separately to the radiators, and there is no need to regulate the heat supply in each individual heating device, since the heat is distributed evenly through the pipes and radiators throughout the entire system. The radial wiring diagram is effective in a one-story building.
The daisy chain solution is based on total number pipes, and if there are few of them, then this type of connection can be implemented. When laying horizontally along the walls, it is difficult to ensure the designer’s original intentions - a large number of pipes will ruin everything. Only decision– hide all wiring under the floor or in the walls at the stage of designing the house and heating. 
The installation and wiring of a two-pipe horizontal heating system has its own secrets:
- This is a long and labor-intensive process;
- It is recommended to connect and adjust the entire circuit for each room before the onset of frost;
- The correct calculation is the heat in the house. Therefore, if you are not confident in your capabilities, contact a specialized company.
The operating principle of the two-pipe vertical system, which organizes heating of the house, is based on the parallel connection of heating points (batteries or radiators). In such a scheme, the presence of an expansion tank is mandatory, as is the routing of pipes along the upper circuit. The hot coolant from the boiler rises through each pipe, reaching all points of the system. The expansion tank is installed in top point heating circuit.
When organizing vertical double-circuit heating, the hot coolant under pressure rises to the top and is then distributed from top to bottom among the heat sources. Cold coolant is supplied to the return line, which is laid lower than the bottom of the heating radiators. This scheme promotes the movement of air through the pipes into the expansion tank and its automatic removal. 
Bottom wiring diagram
When installing a horizontal system, pipes are routed throughout the rooms while maintaining a certain slope - 5-10 mm per 1 meter of pipe. The cooled coolant from the radiators flows through the return line into the pipeline and into the boiler. The difference between this scheme is that there are two main pipelines: one for the supply of coolant, the second for the return supply to the boiler. Hence the generally accepted name for the scheme – two-pipe. 
The water in the system is replenished either through a connected water supply, or manually through the neck of the expansion tank. If it is possible to connect water from the water supply system, then it is better to connect it to the return pipe so that the cold and heated water are immediately mixed.
The operation of such a scheme differs from the distribution at the top in that the coolant supply pipe cuts into the distribution from below, next to the return pipe, and the heated water from the boiler moves through the pipes and radiators from the bottom up - through the return pipes and radiators back to the boiler. If air pockets form in the system, the air is released using special valves embedded in each heating device. 
A two-circuit system with bottom wiring can have one, two or more circuits, and can also be implemented by organizing associated or dead-end circuits. In their homes, owners rarely use these schemes because of their high cost - air vents must be installed on each heating device. Also, heating systems made according to these schemes are equipped with a special expansion tank, through which the air in the system participates in circulation along with the coolant. Because of this feature of the scheme, it is necessary to vent accumulated air masses at least once every 5-7 days. But there is also a big advantage - heating organized according to this scheme can be started even before the construction of the house is completed.
The difference between a double-circuit scheme and a single-circuit scheme lies in the name itself - when a two-pipe heating system operates, two pipes are connected to each heating device, and through the upper heating pipe the hot coolant is supplied to the radiators, and through the lower pipe it is discharged to the boiler when it has already cooled down. The heating scheme for a private house using a dual-circuit system consists of the following components, parts and elements:
- Heating boiler;
- Balance;
- Radiators, registers or radiators;
- Shut-off valve and expansion tank;
- Cleaning filter;
- Pressure gauge and water pump;
- Valve.

The expansion tank is mounted at the highest level of the heating circuit. If water is supplied to the house from an external source and supplied to the pipeline under some pressure, then the expansion tank can be combined with a water supply supply tank. It is also necessary to observe the slope in the return water supply and supply pipes - it should be no more than 10 mm per 2 meters of pipe length - too small a slope will not ensure proper movement of the coolant, and the radiators will take a long time to warm up. Also, a small slope will contribute to the creation of air jams. But if the slope is greater than permissible, then the air will also remain in the system without having time to reach the outlet points. 
If the house has an autonomous double-circuit heating circuit with wiring along the upper contour, then its installation itself can be carried out using different design solutions, depending on where, how and at what height the expansion tank is mounted. The best option can be considered if the expansion tank is located in a heated room and can be easily approached. The top pipe of the horizontal circuit should run as high as possible - preferably under the ceiling, but in such a way that the expansion tank can also be mounted in the house and not in the attic. 
A circuit with two circuits can have the highest efficiency only if the supply pipe is as long as possible. Even with different sizes pipes and other system elements, the efficiency and efficiency of the system will always be high, since the upper connection point of the coolant supply pipe is at the beginning of the heating main.
Also, the efficiency of the system can be significantly increased by including a circulation pump in the circuit. A standard 65-110 Watt pump consumes little electricity, and even with non-stop operation it does not require additional maintenance or repair preventive work. The presence of a circulation pump increases the speed of movement of the coolant, which means heating the rooms. But installing heating according to a two-pipe scheme with an upper circuit makes the inclusion of a pump in the scheme unnecessary and unnecessary.
A two-pipe heating system has a more complex architecture, and its installation requires a large amount of materials. And, nevertheless, this system is more in demand than a simple one-pipe heating system. A two-pipe heating system consists of two closed circuits, one of which serves to supply heated coolant to the radiators, and the second to drain the already used (cooled) liquid. The use of this system is acceptable for all types of buildings, provided that the layout of the premises itself allows its installation.
Two-pipe heating system
Types and advantages of a two-pipe heating system
Technical feature of the heating system of this type is that it consists of two pipelines. One is used to transport coolant heated in the boiler directly to heating sources - radiators. And the second circuit is necessary for the outflow of already used coolant from the radiators - the cooled liquid that has given up its heat.
A double-circuit heating system has a significant advantage over a single-pipe heating system, in which the heated coolant loses some of the heat even before it reaches the radiators.
In a system such as a passing two-pipe heating system, there is an equal temperature of the coolant entering simultaneously into heating devices systems.

Scheme of a two-pipe heating system
Many believe that the cost of a two-pipe system, compared to a simpler one-pipe system, almost doubles - after all, it is necessary to take twice as many pipes. But that's not true. The fact is that in order to properly build a properly functioning one-pipe system, pipes of larger diameter should be used, since they contribute to a more active movement of coolant and waste liquid. And when creating a two-pipe system, pipes of much smaller diameter are used, the cost of which is lower.
The same situation is observed when purchasing additional system components - valves, fittings, connecting elements. Products with larger diameters are more expensive. That is, we can draw a simple conclusion - in fact, purchasing materials for a two-pipe system will not cost you much more than for a single-pipe system. But the efficiency of its work is much higher.

Another significant advantage of a two-pipe system is that in such a heating system it is possible to install valves on each radiator, through which the heating level of the element can be controlled. In addition, using such valves you can also significantly save water and electricity consumption for heating it.
It should be noted that the two-pipe heating system design has another advantage. It lies in comparatively greater aesthetics.
Many owners of houses with a single-pipe system are often upset that a very thick heating pipe cannot be hidden - and this significantly spoils the overall impression of the room. While the pipes used in a more complex two-pipe system are thinner - and hiding them will not be difficult. And even if the pipes are visible, they do not attract much attention.
Considering everything obvious advantages two-pipe system - greater efficiency, low cost and aesthetics, you can confidently choose it. This is what most owners of country houses do.

There are two types of two-pipe heating systems - horizontal and vertical 2-pipe heating systems. The main difference between these types is in the axis of the pipeline location. These pipes are used to connect all elements of the heating system. Of course, each type has its own disadvantages and advantages. Common to both types are the following advantages: excellent hydraulic stability and high level heat transfer.
Should be installed in one-story buildings where the heating pipeline is quite long. In such houses, connecting heating radiators to a horizontally located system is the most practical solution question.

It is slightly more expensive than the horizontal one. However, since the riser is located vertically, this allows it to be used even in multi-storey buildings. In this case, each floor separately cuts into the central heating riser. In addition, the advantage of the vertical type of heating system is that air does not accumulate in it - if bubbles arise, they immediately rise vertically, directly into the expansion tank.
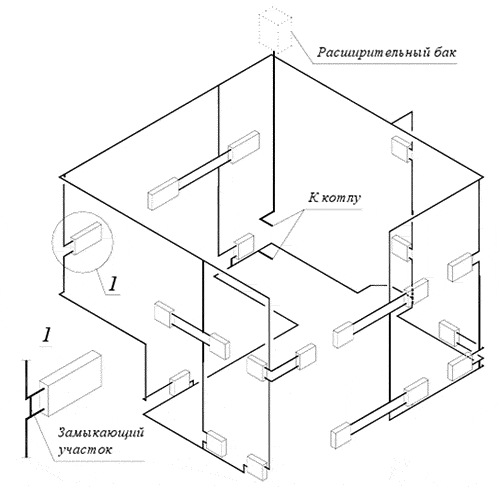
Whatever type of system you choose, you should keep in mind that balancing must be carried out. When choosing a vertical system, balancing a two-pipe heating system requires the riser itself. When it passes horizontal adjustment two-pipe heating system, loops are exposed to it.
Types of wiring for a two-pipe system
Regardless of which type of two-pipe heating system you choose for own home, there is another system for dividing it - according to the principle of organizing wiring. In the photo you can see two different schemes wiring Each has its own advantages and disadvantages of a two-pipe heating system.
In this case, the pipeline with hot coolant is laid in the basement or basement. It is also possible to lay pipes underground. With this type of installation, it should be taken into account that the pipes for returning the waste coolant back to the boiler must be located even lower. Using the principle horizontal wiring provides for the need for some deepening of the boiler - only in this case will water move from the radiators to heating element as quickly as possible. In addition, there is a need to connect an additional line - an overhead line - to the circuit. With its help it will be possible to remove air from the system.

To construct it, it is necessary to place the expansion tank at the highest point of the pipeline. The branching of the system is also carried out there. Being more practical, overhead wiring cannot be installed in buildings that do not have an attic.
You can choose the most suitable type of wiring, regardless of what type of supply pipe arrangement is used in your home.
However, there are some requirements that should definitely be taken into account. In particular, for houses in which a two-pipe system is installed vertical system heating, the most appropriate is to use lower wiring. This is explained by the fact that two-pipe heating with bottom wiring allows maximum benefit use the pressure that arises in the system when there is a fairly large difference between the coolant and waste liquid. Of course, if architectural features buildings do not allow the use of lower wiring, the use of upper wiring is acceptable.

It should be taken into account that the use of upper wiring both for supplying coolant to radiators and for returning return to the boiler is not The best decision, since sludge may accumulate in the lower elements of the system.
In fact, the classification of a two-pipe heating system is very multifaceted.
Another principle of separation is the direction of coolant flow. According to this criterion, the system can be:
- direct flow. In this case, the direction of movement of the coolant and return coincide.
- dead end. When using a scheme such as a two-pipe dead-end heating system, the hot and waste coolant move in different directions.
Modern systems can be equipped with a special pump, thanks to which the coolant moves more actively. At the same time, natural circulation systems are also often used, in which optional equipment does not apply. If you intend to use a two-pipe system in two-story house, then this dual circuit heating must be equipped with a pump.

Heating system with circulation pump
But when installing a two-pipe heating system in one-story room you can do without a pump, using some laws of physics to move the coolant naturally. It is important to take into account that for more active natural circulation of the coolant, it is necessary to lay heating pipes with a slope directed towards the heating boiler.
However, regardless of the system you use (with forced and natural circulation), a slope must be present.
For systems with forced circulation, it is necessary in case of an unexpected power outage or pump breakdown. In this case, the slope allows the coolant to circulate naturally.
Calculation
When planning a two-pipe system, it is important to carry out a preliminary calculation of the two-pipe heating system, using such a guide as a preliminary diagram of the system (all elements must be indicated on it) and special axonometric formulas and tables.

This simple hydraulic calculation of a two-pipe heating system allows you to determine the optimal diameter of the pipes necessary for the normal functioning of the system and the volume of radiators used. The most commonly used types of calculations are:
- by pressure loss. This method assumes an equal level of coolant temperature in all parts of the system.
- calculations taking into account the value of conductivity and resistance. In this case it is assumed different meaning temperature indicators.
As a result of using the first method, you can obtain very accurate data showing the level of resistance in the circuit. The second method shows the temperature in each individual segment of the system, as well as the approximate coolant flow.
Principles of installation of a two-pipe system
When installing a two-pipe system, a fairly large number of requirements and rules should be taken into account. Only their full compliance will make it possible to create the maximum effective system heating and produce correct installation two-pipe heating system:
- two-pipe closed system heating or open circuit consists of two circuits - the upper one serves to supply heated coolant to the radiators, and the lower one serves to drain the waste liquid.
- pipes should be laid with a slight slope. It should be made towards the last radiator of the system.
- the upper and lower lines must be parallel.
- the central riser must be insulated - otherwise there will be a loss of coolant at the stage of its movement to the radiators.
a two-pipe reversible heating system must have several taps that will allow water to be drained from individual areas if repairs become necessary.
- the pipeline should contain as few corners as possible.
- The expansion tank should be located at the highest point of the system.
- taps, connections and other elements of the system must be equal to the diameter of the pipes used.
- in case the pipeline is used steel pipes, it is necessary to create a system of fasteners that will support the pipe. The distance between supports should not exceed 1.2 meters.

The sequence of connecting elements in how to make a two-pipe heating system is simple:
- A central heating riser is connected to the heating boiler.
- in the upper part, the central riser is connected to the expansion tank.
- A splitter comes from the tank, directing the pipes to the radiators.
- the waste liquid discharge line is laid parallel to the supply pipes. It should be cut into the bottom of the heating boiler.
- the pump is installed at the most convenient point - most often at the inlet (outlet) of the boiler.
This type of heating system is quite efficient. Today there are a large number of boiler models that require automatic control of the coolant heating level. You can watch a video on how to make double-circuit heating with your own hands below.




