Live in own home has significantly more advantages than even the most luxurious apartment. A private house– a place where you are free to do whatever you want. Here you will not be disturbed by noisy neighbors who want to do repairs early in the morning or late at night. Here you do not run the risk of being flooded or experiencing the inconvenience that apartment residents face. Many people are accustomed to believing that buying a plot of land, much less building a house on it, costs fabulous money. However, with the development modern technologies in construction, the cheapest technology for building a house has become several times more accessible. Now we will look at the main question: where to start, and most importantly, what to build the cheapest house from?
Preparatory stage
The first point that needs to be determined initially is the functionality of the house. What is it for?

If this is a country cottage for seasonal residence, then you need only materials,

if this is a full-fledged home for permanent residence, then completely different.

To decide what kind of house will be, you should thoroughly study the climate and weather conditions of the region where construction is planned. After all, the choice of building materials directly depends on the temperature conditions throughout the year. For regular living, a house must be constantly heated during the cold season, which entails certain financial costs. Therefore, when choosing a material for a building, you should be guided by thermophysical properties: thermal conductivity and heat capacity, as well as shrinkage.
Each climatic region has its own temperature regime, wind speed and protection class based on the level of thermal insulation properties. Therefore, when choosing a material and calculating the thickness of the walls, you need to be guided by two main parameters: the coefficient of thermal resistance and thermal conductivity.

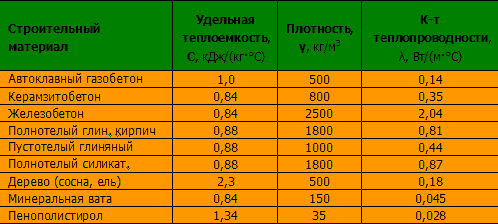
For each region, its own specially calculated thermal resistance index of the CTS is used. In order to gain clarity on upcoming heating costs, you need to calculate the CTC future design. To do this, the width (δ) of the wall is divided by the thermal conductivity coefficient (λ), which is indicated in technical specifications building material R = δ/λ. The calculated value of heat transfer resistance must correspond to the standard value.
As an example, consider using cellular concrete, which has a thermal conductivity coefficient of 0.12 W/m* ºС. Let's take a block 0.3 meters thick and calculate: R = 0.3/ 0.12 = 2.5 W/m2 * ºС. This figure is below the norm and is only suitable for construction in the southern regions of Russia. A block 0.4 meters wide gives a heat transfer resistance of 0.4/0.12 = 3.3 W/m2 * ºС, which is slightly higher than the standard value and can be used in the construction of buildings in Moscow and St. Petersburg. The calculation is relevant only when laying blocks on glue.
The wall thickness corresponding to the best generally accepted standards in terms of energy efficiency can be determined using the same formula, where it will be equal to the product of the heat transfer resistance value and the thermal conductivity coefficient δ = λ x R.
From this it follows that in order to obtain the standard value of resistance λ = 3.2, the wall thickness is from solid wood coniferous species(pine, spruce) will be 0.18 x 3.2 = 0.576 m, from brick 0.81 x 3.2 = 2.592 m, and from concrete 2.04 x 3.2 = 6.528 m. In this case, the mineral wool insulation is thick 140-150 mm corresponds to the standard: 0.045 x 3.2 = 0.14 m.
Therefore, when choosing a material and determining the thickness of the structure, heat transfer resistance and thermal conductivity should be taken into account.

Coefficient of thermal conductivity,
specific heat

and change linear dimensions different for each material.
In addition, when choosing materials for construction inexpensive home, you need to study the market for building materials specific to a given region. Delivery of materials, as a rule, takes up a significant share of their cost.
Now you need to decide on the size of your future home. For example, do you want to build cottage inexpensive or the house will have more floors. What will be the area of the house in relation to the area of your plot?
You can calculate the area of your plot online.
Windows of standard sizes;
Practical layout without frills;
Simple roof;
Available building materials;
Flat small fireplace;
One should also take into account important nuance, if you have small area, then you can choose a simple project two-story house. This solution will be much cheaper than building a one-story large house.
The cost of a future home is determined by three components, on each of which you can save:
- the architectural layout is compact, maximum functionality and comfort and allows you to achieve 20% savings;
- simple constructive solution must be rational and not contain any architectural frills will provide another 10% savings;
- modern materials make it possible to use the latest technologies in construction, allowing you to do the work yourself or with the involvement of a minimum amount of outside labor, which guarantees up to 40% savings in the final result.
The optimal solution for a family of 2-3 people is housing consisting of three rooms with a total area of approximately 50 m2. A suitable option could be a 6x9 house, including: two bedrooms, a living room in the form of a studio, with a kitchen, a combined bathroom and toilet, and small hallway.
<
Layout: maximum functionality and comfort
The main principle of space planning is to extract maximum benefit from every square meter of space. In our case, this is the ratio of total and usable space. This house, consisting of three rooms with a total area of 54 m2, will fully satisfy your needs for modern housing. Moreover, the ratio of total and usable area (52 m2) is 96.3%.

But over time, you will want to increase its area. This structure is most suitable for transformation. It can be expanded in width and height.


Second option
Important! The construction of the second floor must be thought out in advance in order to lay the appropriate foundation.

Third option, first floor

Third option, second floor

Exterior view of the house, economy option

Exterior of the house after expansion 
The key to savings: simplicity of design
Designs should also be approached as simply as possible, without additional frills. When building economically, there are a number of points that need to be taken into account:
- The selected house width of 6 m will allow you to install floor slabs without difficulty. The standard size will not require the construction of an additional load-bearing wall.
- Combining the dining room, kitchen and living room into a modern living room, according to European standards, will save on the absence of walls and doors.
- A sufficient width of the walls will be 30 cm, and heat resistance can be achieved due to the thickness of the layer of thermal insulation material when cladding the house. In this case, the width of the base is reduced to 25 cm.
- It is advisable to make the walls in the house from plasterboard; they do not require a foundation and are easy to install.
- The roof is made gable, without unnecessary frills - this is the most cost-effective design.
Building a cheap house with your own hands is the most economical option
Approximately half of the construction costs are fees for performing the work. When building a cheap house, it is more advisable to do the maximum amount of work with your own hands, without the involvement of hired workers.
Why do you need to purchase only modern material? Its installation technologies are designed for the average person, so construction will not require professional skills from you and will provide an opportunity to save money. One assistant can be recruited as labor. If you do not have free time to build a house with your own hands, hire a team of two people with appropriate qualifications, retaining control over the work.
Another option is to build according to standard designs. Here you do not need to participate in construction; it is enough to accept the finished house into operation, be sure to draw up an acceptance certificate for the work performed, specifying the developer’s warranty obligations.
This 6x9 house is a great version of a two story conversion.
Reviews and disputes: which cheap house is better?
To explain which cheap house is better, we suggest you read the comments we collected from various forums:
Alexander V.
I want to talk about building a cheap house. Moreover, I will touch upon not only the monetary side of the issue, but also the labor-intensive one. We buy modern materials, preferably from a construction hypermarket, where prices are much cheaper. We discard ideas about buildings made from scrap materials (clay, straw, wild stone) as untenable. In the 21st century, we can talk about clay walls and rubble foundations. We're talking about modern housing, not Grandpa Pumpkin's house. We won’t even consider the environmental friendliness of building materials. At the time of the developed world wide web, you can find the most conflicting opinions about any material.
We will not consider hired builders either. This multiplies the estimate by at least two times initially. We carry out the construction ourselves; anyone can do it. The question is the duration of the process.
And so the foundation. When building a house you cannot do without it. The most appropriate and cost-effective is a strip foundation on piles. The task is not difficult. Every 2m we drill piles, the length depends on the soil, and fill in the grillage.
Still, the cheapest construction will be a frame house insulated with mineral wool or expanded polystyrene. Building a house from brick or sides with cement mortar will increase the cost of the estimate, take a lot of time, and as a result we will get a cold structure that requires insulation.
Bogdan S.
I was going to build a 6x9 house. For two months now, I have been working on a personal project and drawing up a construction estimate. I read smart books, participate in forums on all topics of interest, and watch videos. Now I’ve read it and understand that I have everything as you said: a pile foundation, a frame house, a slate roof. Interior finishing: plasterboard, OSB boards and wallpaper. Of course, plus heating and lighting. One thing I can say is that I am not investing in 10 thousand conditional raccoons. A bit more.
Sergey Zh.
I developed a project for a 50 m2 house for a friend of mine. Nothing special, a budget option, but a home for year-round use. The foundation is solid. Wooden frame house insulated with mineral wool. There is a vapor barrier film on the outside, hardboard on the inside. The roof is slate. Quite a warm building, suitable for winter use. The appearance is not very good. Just covered with vapor barrier. You can subsequently cover it with siding. But the budget is the most modest. An acquaintance spent only 4 thousand USD. True, I built it myself, I didn’t even want to hear about any hired crew.
Looking at my house, I am increasingly convinced that it is unlikely that anything can be built cheaper than a frame house. I insulated the walls, rollers, and roof with 15 cm thick mineral wool. In addition, I built an attic floor. My roof is the simplest gable roof, covered with zerolin. The outside was finished with siding, and the inside was covered with OSB and wallpaper. It cost me the pleasure of $9500.
The frame is the cheapest and warmest, but this does not mean that it is free. Everything is relative. Some friends of mine built a house from sibit. They were happy until winter came. They were frozen through the winter, and now they are deciding how to insulate themselves and what it will cost.
Of course, the main costs are building materials, which we will talk about in more detail.
Modern building materials are the cheapest way to build a house
There is enormous competition in the modern building materials market. Therefore, having made a short walk around the main points of purchase, building materials such as a hypermarket, bazaar or warehouse, it will not be difficult to find the most reasonable price. But different materials differ significantly in price.
The author of the article does not pursue the goal of promoting this or that building material, since the site is not engaged in their sale. The main thing is that a person with a limited budget for construction can become the owner of a good and solid home.
Before reading the various house options, pay attention to Compared to other houses, it is cheap to build.
Cheap brick house?
- Brick.

As many people know, brick is one of the most durable, but also the heaviest materials. Based on this, it has both advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages:
- high strength and durability;
- excellent sound insulation;
- availability;
- environmental friendliness.
Flaws:
- large mass - a solid foundation will be required;
- insufficient energy saving;
- difficult to process;
- long process of building a building.
Modern brick allows you to build a house of any size and design.
Cheap steel structure house
- Durable steel structures.

Today it is one of the most durable and affordable building materials, which allows you to build reliable structures, houses, etc. in the shortest possible time.
Advantages:
- affordable price;
- quick and easy installation;
- versatility - you can build any structure;
- Using modern finishing materials you can create a unique exterior.
Flaws:
- low strength;
- poor thermal insulation and sound insulation without additional insulating materials.
Durable steel structures today are becoming increasingly popular in the construction of private houses.
Cheap wooden house - is it true?
- Log or timber

A modern, stylish house made of logs looks amazing, and its high environmental friendliness, strength and thermal insulation make this building material stand out from others.
Advantages:
- high strength;
- environmental friendliness;
- excellent sound insulation;
- quick and easy installation;
- high thermal insulation;
- easy to process;
- relatively light weight;
- amazing appearance.
Flaws:
- price;
- the need for additional treatment against pests;
- fire hazard without special impregnations;
- low hydraulic stability.
A modern house made of logs or beams is stylish, practical and comfortable.
Favorite: cheap house made of foam concrete
- Foam concrete is the most profitable material for building a house.

A lightweight building material that surpasses others in its characteristics.
Advantages:
- quick and easy installation;
- high load capacity and low weight;
- high strength over time;
- excellent sound and heat insulation;
- light weight;
- reasonable cost;
- easy to process;
- environmental friendliness.
Disadvantages:
- the first few years after manufacture it has low strength;
- the porous structure of foam concrete will require additional finishing work;
- hot in summer.
Foam concrete is the cheapest way to build a house.
We looked at some of the most affordable building materials that can be used to build an inexpensive home. Today they are also widely used: twin blocks, monolith, ceramic stone, etc.
For example, the cost of a one-story frame house with two rooms, a kitchen, a living room and a bathroom will cost 600-700 thousand rubles. Thus, the cheapest frame houses can be built for relatively little money.
We also recommend:
Let’s immediately make a reservation that in this article we will not consider exotic building materials, such as adobe brick, reed or felt. Let's talk about materials traditionally used in Russia and most other countries for building houses. There are quite a lot of them (and new ones are constantly appearing), however, they are all some variation on the theme of wood, stone or concrete.
The traditional debate about which walls are “warm” and which are not, in our opinion, has already lost relevance: on the one hand, there are now so many effective thermal insulation technologies that it is possible to make any wall “warm”; on the other hand, even the “warmest” wall, made in a “clunky way”, will produce only drafts instead of warmth. Therefore, we believe that one of the most important qualities that the best material for building a house should have is its weight. The more massive the walls of the house, the stronger they are and the greater the load they can withstand. But the foundations in such a structure must have a high load-bearing capacity, which significantly increases the cost of construction (the cost of the foundation can reach up to 30% of the cost of the entire house!)
Wooden houses
The “lightest” types of houses are frame-panel and panel. Their walls and partitions consist of a wooden frame, upholstered with wooden panels, between which there is a layer of heat-insulating material. The difference between them is that the walls of a frame house are built “on site”, while the walls of a panel house are built in the form of panels at a factory. The advantages of such houses are: speed of construction (professional teams spend about 3 weeks on assembling a frame house, a panel house can be assembled in a few days), the possibility of using easy-to-install weak-bearing foundations, and, consequently, a significant reduction in the cost of the structure. Disadvantages: weak strength and load-bearing capacity (it is allowed to build up to two floors with an attic), fragility (the guaranteed service life of such houses is approximately 20-25 years, although in reality a well-built house lasts 50-60 years without repair - there are examples). In addition, in Russia frame-panel technologies are still viewed somewhat warily, although in Europe and America these are one of the most common houses, so wooden panels may well act as the best material for building a house with the tolerance of certain structural restrictions.
Next in weight are wooden log houses, either from round logs (manual or mechanical cylinders) or from rectangular timber. Their advantages: ease of construction, average cost, the ability to use inexpensive foundations, increased strength and durability compared to frame houses (minimum 40-50 years). The disadvantages are the following: log houses are subject to shrinkage, so it is impossible to build such a house within one season; As a result of shrinkage, cracks are formed, so log houses require mandatory caulking; increased fire hazard of the material, requiring the use of additional protective measures; the most important thing is the direct dependence of the quality of the material on its price. Inexpensive hand-fed log houses are usually made of low quality wood, with numerous cracks, and good quality logs and beams are usually expensive.
Houses made of stone and concrete
Recently, houses made from various types of concrete derivatives have become widespread: foam concrete, polystyrene concrete, etc. These materials are quite light (compared to ordinary concrete), non-flammable, have good heat and sound insulation, are easy to install and also claim to be the best material for building a house. One of the disadvantages is the fragility of the material, which does not allow building higher than two floors. Problems arise with the interior decoration - the “softness” of the material forces us to make various kinds of additional “false walls”. In addition, buildings made from these materials require the immediate installation of insulated facades, otherwise unprotected walls begin to quickly collapse.
In our country, individual construction has been actively developing in recent decades. In addition to the construction of warm and durable houses from classic wood and brick, new materials and technologies are increasingly being used, primarily borrowed from abroad.
New materials for house construction are being developed to simplify and speed up installation and increase the heat-saving characteristics of external walls. But the low cost of the material for constructing the building frame and its good technical characteristics alone do not guarantee that the final costs will be small and the house will turn out warm and cozy.
To choose cheap materials for construction, the following factors are taken into account:
- Climate and location of the building site. This factor influences the choice of wall thickness and the need for additional insulation.
- Soil type. Affects the choice of foundation and the technology of waterproofing the underground part.
Thus, it is important not only to compare the cost of materials for building structures, but also to determine which is the cheapest option suitable for specific operating conditions.
Final cost of work
It is the final cost of the work that should be taken into account when assessing the characteristics and cost of materials for building the walls of a house and looking for the most budget option.
The final construction costs are made up of a number of components:
- Architecture – the simpler, the cheaper.
- Engineering solutions – selection of the optimal design option for each design.
- Internal layout is a rational approach to using space to get the maximum usable area.
- Insulation - the need and costs depend on the thermal conductivity of the walls.
- External and internal finishing - the need depends on the characteristics of the wall material; you can save money when choosing finishing materials.
- Building materials – it is on their choice that developers try to save as much as possible.
- Foundation - costs account for up to 40% of the total investment in construction; the parameters of the foundation depend on the choice of materials for installing the building frame and roofing system.

If you want to reduce construction costs, keep in mind that choosing a cheap material for building walls may result in the need to spend extra money and time on their insulation and finishing. When building a house higher than one floor, the strength characteristics also require special attention.
The cheapest materials for construction
Building a classic brick house will not be cheap - the piece material for laying the walls itself is expensive, and a solid foundation is required. Plus, the installation itself will take a lot of time and will require the involvement of professional masons if you want the house to be durable, warm and last for at least 100 years.
Today, new materials and technologies are being used, thanks to which the construction of a private house will require a minimum of time. These include the construction of walls made of monolithic concrete using permanent formwork made of foamed polystyrene. Steel reinforcement is installed inside the polystyrene foam blocks with a tongue-and-groove connection.
The foam material acts as insulation; the cavity between the walls is filled with concrete, thereby forming a monolithic frame of the building. The materials themselves that are used for construction (concrete, polystyrene foam, reinforcement) are affordable, but the increase in price occurs due to:
- quite high cost of finished blocks with installed fittings;
- need to hire a concrete truck.
In addition, such a house requires external and internal finishing, as well as the installation of a high-quality ventilation system, since walls with a double layer of polystyrene foam do not breathe. This is an example of how cheap materials do not guarantee savings during construction and comfort in the home.

Expecting to find the cheapest material for building a house, you should pay attention to structures made:
- from foam blocks;
- from expanded clay concrete;
- from gas silicate blocks;
- using frame technology;
- from timber;
- from rounded logs.
To evaluate which material is better, you should compare the pros and cons of each option.
Foam block
The popularity of foam concrete is explained by its affordable price and simple installation - no special tools or lifting equipment are required to build a house, since the weight of the block does not exceed 25 kilograms, and it can be cut with a regular hacksaw.
The list of advantages of foam blocks also includes:
- savings on the foundation - wall structures weigh relatively little, which makes it possible to equip a lightweight underground foundation;
- high installation speed;
- strict geometry of the blocks (if the material is of high quality) - due to this, the thickness of the seams is minimal, which reduces the consumption of adhesive, increases the strength of the masonry and reduces the thermal conductivity of the walls;
- high thermal insulation parameters - the porous structure prevents heat loss through the walls;
- vapor permeability – the material “breathes”, resulting in a comfortable microclimate in the room;
- environmental friendliness and fire safety - the material does not burn and does not emit harmful substances.

Disadvantages include:
- the need for external cladding - the building needs external finishing, since the porous material absorbs moisture and freezing and thawing cycles do not benefit it;
- in cold climates, the walls of the house need to be additionally thermally insulated, while insulated ventilated facades increase the cost of construction, pasting with polystyrene foam boards will be inexpensive, but the walls will become vapor-tight and a supply ventilation system will be required;
- the risk of blocks cracking during shrinkage of the house if insufficient quality material is used.
Manufacturers claim that the service life of foam block buildings reaches 80 years. But the material appeared relatively recently, so there is no information about its actual durability.
Expanded clay concrete
Hollow expanded clay concrete blocks are used for external walls and partitions of a private house. If we compare expanded clay concrete with foam concrete, then expanded clay concrete is more difficult to process and is heavier, which should be taken into account when calculating the foundation. The size of the expanded clay concrete block is larger, which speeds up installation.
Expanded clay concrete is characterized by:
- environmental friendliness and health safety;
- resistance to combustion, biological damage;
- good noise insulation and heat insulation properties;
- breathability.
Walls made of this material require external cladding. Finishing allows you to make the facade aesthetically attractive and protect the porous material from damage when wet and subsequent freezing. Interior finishing of the premises is also required, but it should be taken into account that fasteners do not hold well in expanded clay concrete.

If the masonry is not done well enough, or the material has cracked as a result of shrinkage, cold bridges arise and the walls of the house need additional thermal insulation.
Aerated concrete
Trying to find the cheapest building material, developers buy aerated concrete - lightweight blocks that are easy to install. It is important to use autoclaved aerated concrete from a trusted manufacturer - materials made by drying in a hydration chamber have 3 times lower strength and can only be used as insulation.
The blocks must be even, since the seams are cold bridges. But even if the masonry is made with minimal joint thickness, the house needs to be insulated if there is a desire to reduce heating costs. External and internal decoration of walls made of porous aerated concrete is required.
The advantages include the ease of processing blocks. At the same time, during transportation of material and construction work, care should be taken - the blocks are not resistant to mechanical damage.
Frame house
To build a house using frame technology requires the use of a whole set of building materials, usually these are:
- lumber for mounting the supporting frame;
- heat insulator, which is laid inside the walls;
- sheet material for external and internal cladding (OSB boards, etc.).
Frame house construction has a number of advantages. During construction, there is no need to use equipment or specialized tools; the work is completed in a short time. The load on the base is small, so a lightweight foundation is used. It is convenient to install communications in a frame house - they are hidden inside the wall. A structure erected using this technology does not require time to shrink.

This construction option is not without its drawbacks. If foamed polymer insulation is installed in the walls, the house does not “breathe,” which affects the microclimate. Mineral wool is vapor permeable, but it absorbs moisture and, as a result, its thermal insulation properties are reduced.
To protect the insulation from getting wet, it is necessary to install a vapor barrier on the side of the room. It is better to use a special membrane that allows air to pass through but retains moisture. This is noticeably more expensive than using polyethylene, but contributes to a good microclimate in the house.
Having saved on the construction of walls, you will have to spend a lot of money on external finishing, since the sheathing of the frame should be reliably protected from atmospheric influences. The service life of such a house depends on how well the wooden frame elements are treated against biological damage, on the choice of external finishing, and on the quality of construction work.
timber
A wooden house is warmth and home comfort, a unique microclimate, thanks to the use of natural wood for construction.
For the construction of a log house, the following types of timber are used: simple (natural moisture or dry) or glued, consisting of several lamellas. Today in house construction it is customary to use profiled timber, which allows you to connect crowns without ventilated cracks.

When choosing timber, you should consider that:
- a house made of wood with natural moisture shrinks greatly, including deformation of the crowns, with the formation of cracks in the frame, the timber cracks;
- dry material is resistant to cracking and deformation;
- a structure made of laminated veneer lumber practically does not shrink or deform; finishing can begin immediately after roofing work is completed.
You can build houses from profiled timber yourself; the material is easy to process. But the thickness of the walls is usually not enough to allow a house to be used all year round in a cold climate without additional insulation - otherwise you will have to spend more money on heating.
Rounded log
When trying to find the best material for building a house, you should pay attention to rounded logs. The use of this material makes it possible to seriously reduce the final construction costs, because:
- the weight of the structures is not the greatest, so a reinforced foundation is not required;
- for the construction of a log house, large-diameter logs are used, the thermal conductivity of which makes it possible to do without additional insulation of the walls;
- even, smooth logs look attractive, the house looks great without any external or internal decoration.
A rounded log is a good option for construction if you order the production of a log house kit. In this case, a numbered “constructor” is delivered to the construction site, where all elements are manufactured using modern equipment, that is, all connections are made with high precision. The material used is treated with special agents that protect the wood from biological destruction and increase fire resistance.

If you want to live in a house where an optimal microclimate is always maintained (cool in summer, warm in winter, the air does not dry out or become waterlogged), it is recommended to choose.
Conclusion
The choice of material for building a house affects the speed and cost of building the box, the quality of life in the house, and the durability of the building. The desire to save on material for wall structures can result in increased costs for insulation and finishing. If a house is being built on its own, the ease of installation and the need to use specialized tools are assessed.
To choose the right material for building a house, you need to know a few key points:
- heavy houses require a strong and deep foundation;
- lightweight buildings are less durable and require additional insulation;
- the heavier the material, the more expensive it is to work with it;
- Sometimes transport accessibility has the greatest influence on the choice of material.
When choosing materials, you need to proceed from the financial feasibility and construction time frame. The absence of “wet” work significantly speeds up the construction of a house and can reduce the cost of construction. It is also important to consider the region of construction. Not so much because of the climatic conditions, but because of the popularity of a certain material.
For example, if there is one or even several brick factories nearby, then bringing wood from afar will be more expensive than building with red brick. If a house is being built in a forest area, then frame-panel projects will not always be cheaper than a real log house. But often it is necessary to build only from imported materials. And then it would be useful to study their properties.
Wooden and frame houses
If you choose wood for the walls of your house, you can be sure that the material is environmentally friendly. The microclimate in a pine log house is truly special. But building a house from a solid log on your own is quite difficult.


But they need to be treated with antiseptic compounds, otherwise the walls will be exposed to all atmospheric phenomena. And this means an increase in construction costs.
Houses made of wood or metal frames are the easiest to assemble. Frame-panel houses made of SIP panels are especially convenient.

But installation will require loading equipment, so this option is not suitable for self-construction. On the other hand, a large five-room house can be assembled in a week or a week and a half, and due to its light weight, it does not require a strip foundation buried one and a half meters deep.
Brick and ceramic blocks
If the question arises, which material is the most durable, then the answer is simple - red clay brick. A brick house will last for more than a hundred years; it can be inherited from generation to generation. But the price of building a brick house is impressive.

A more modern material is ceramic blocks. Despite their high cost, they are much more profitable than traditional bricks, since one ceramic block weighing 25 kg replaces 15 bricks with a total weight of 50 kg!

Houses made from these environmentally friendly materials have a high heat capacity of the walls, so it will take a long time to warm up a fairly cool house. But then, even when the heating is turned off, the walls will give off heat. When building from porous materials, insulation is not required - the air in the cavities is natural thermal insulation. Due to their heavy weight, brick houses require a deep and strong foundation - a pile or reinforced concrete strip foundation. And these are additional costs.
Gas blocks
Aerated concrete blocks are an excellent alternative to brick. They are lightweight and durable, and the air bubbles in the blocks provide natural thermal insulation. This is a lightweight and durable material; one block weighing 18 kg replaces 20 bricks weighing 70 kg!

But due to their high hygroscopicity, it is important to prevent moisture from entering the aerated blocks during storage and to provide good waterproofing of the facade.
Comparison of materials
So what to choose for construction? A brief description of:
- solid log - does not require processing, an environmentally friendly, but difficult material to build with your own hands;
- processed wood - easy to assemble, but requires increased care, short-lived (about 25-50 years);
- frame house - inexpensive to build, but fragile and relatively short-lived (up to 70 years of service);
- brick and ceramic block are durable and reliable, but expensive materials;
- aerated block is a more economical material compared to brick, but still more expensive than frame construction.
The advantages of brick, ceramic block and gas block are described in detail in the video:




