Main symptoms:
Gonorrhea in men (syn. gonococcal infection, fracture, gonorrhea) - infectious- inflammatory process, affecting the organs of the genitourinary system. Suppuration of the mucous membrane occurs, causing characteristic symptoms. Self-medication in this case is impossible, since it can lead to serious consequences, in particular infertility.
The causative agent of gonorrhea in males is gonococcus, which is predominantly sexually transmitted. However, there are several other mechanisms of infection.
The symptoms of gonorrhea in men are specific, the most typical being whitish discharge from the urethra. The clinical picture includes frequent urge to defecate Bladder, which cause pain, cramps and discomfort.
The basis of diagnosis is the results of laboratory tests. Diagnosis must necessarily include a physical examination of the male genital organs and several instrumental procedures.
Treatment of the pathology is carried out using conservative methods - the patient is prescribed medications for oral administration. It is important to remember that both sexual partners must undergo therapy.
Etiology
The causative agent of gonorrhea in men is a specific microorganism - gonococcus. Most often, the bacterium lives and multiplies on the lining of the organs of the urinary system, but can be found in the secretion of the prostate, seminal vesicles, oral cavity, on the mucous membrane of the eyes and rectum. The bacterium can penetrate the blood, where it quickly dies, but manages to harm blood vessels. It is impossible to say for sure how many days later it appears.
The pathological microorganism is characterized by instability to environmental conditions, which is why outside human body dies quickly.
The gonorrhea provocateur has the following features:
- survives for 24 hours on damp towels or sponges, but this infection mechanism is extremely rare;
- heating from 41 to 50 degrees after 6 hours leads to the death of gonococci. It is noteworthy that a sick person may have a fever, in which the temperature increases to 41 degrees, but this only slightly weakens the pathogen;
- optimal temperature for reproduction - 37 degrees.
The source and carrier of the disease is a sick person. Infection can occur in several ways:
- Sexual. 99% of all cases of infection with gonococci. The nature of sexual contact does not matter: the pathogenic agent enters the body of a healthy person both during vaginal, rectal or oral sex. Men become infected from a sick woman in approximately 40% of cases, which is explained by the structural features of the genitourinary system. The likelihood of infection is higher if the partner is menstruating, and sexual intercourse is long and has a violent ending.
- Bytovym. Infection occurs through contact with personal hygiene items, such as bath accessories or bedding.
- Vertical. Gonococcus is transmitted from mother to child during childbirth, as a result of which infants may be diagnosed with congenital gonorrhea.
Risk factors that increase your chances of developing symptoms:
- promiscuous sex life;
- homosexuality;
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- reluctance to use condoms;
- use of other people's funds intimate hygiene;
- visiting public toilets and baths;
- failure of the immune system.
Gonorrhea in males rarely occurs in an isolated form, which is why it can be combined with the following infections:
- viral diseases.
Gonorrhea is most often diagnosed in people between 20 and 30 years of age.
Classification
Based on the age of manifestation of characteristic clinical signs, it is customary to distinguish the following types of disease:
- Fresh gonorrhea - infection occurred less than 2 months ago. In such situations, it is important to know how long it takes for the first signs of gonorrhea to appear in men: symptoms usually appear approximately 3 days after infection.
- Chronic gonorrhea in men - infection occurred more than 2 months ago. Exacerbation of the disease can be influenced by sexual arousal, drinking alcohol, poor nutrition and sexual contact.
Depending on the course of gonorrhea, it can be:
- acute - symptoms arise suddenly and unexpectedly;
- subacute - there is a gradual development of symptoms;
- torpid or sluggish - clinical signs are mild or completely absent;
- latent or asymptomatic carriage of gonococcus - the presence of the pathogen in the body is established only through laboratory tests.
According to the localization of the infectious-inflammatory process, they are distinguished:
- gonorrhea of the genitourinary system;
- damage to the glans penis and inner layer of the foreskin;
- gonorrhea of the epididymis and prostate gland;
- gonococcal perihepatitis;
- gonorrhea of removable vesicles;
- gonococcal and;
- gonococcal and;
- gonococcal and;
- gonococcal and .
There are complicated and uncomplicated course of gonococcal infection.
Symptoms
The incubation period for gonorrhea in men varies from 1 day to 3 weeks, but most often it is 3–5 days. With a latent course, clinical signs may be completely absent, which is why the pathology often becomes a diagnostic discovery. Detection of gonococcus in the body occurs during a preventive medical examination or in the process of diagnosing a completely different problem.
Among the classic symptoms of gonorrhea in men are:
- whitish or purulent discharge from the urethra;
- frequent urge to empty the bladder;
- swelling of the scrotum;
- cramps and pain that appear when urinating;
- spread of pain to the entire groin area;
- the occurrence of erosions on the head of the penis;
- , less often ;
- the appearance of blood in urine or semen;
- irritation and dryness of the foreskin;
- increased sensitivity during sexual intercourse;
- increase in the volume of regional lymph nodes;
- periodic false urge to urinate;
- urine retention;
- pain during defecation;
- weakened erection;
- decreased orgasm;
- frequent wet dreams;
- promotion temperature indicators;
- general deterioration of health.

These signs are observed when the infection is localized in the organs of the genitourinary system. It should be noted how gonorrhea manifests itself in men when the inflammatory process spreads to other areas:
- pain under the right ribs;
- attacks of nausea and vomiting;
- sore throat;
- swelling and redness of the eyelids;
- photophobia;
- increased tearfulness;
- pain, itching and burning in the anal area;
- mucopurulent or bloody discharge from the anus;
- pustular rashes on the upper and lower limbs;
- severe pain in the affected joint;
- swelling and redness of the skin over the sore joint.
Chronic gonorrhea is characterized by a protracted course with periods of exacerbation of symptoms. Among the manifestations, it is worth highlighting adhesions in the pelvis and a decrease in sexual desire for the opposite sex.
Diagnostics
Only a venereologist can make a correct diagnosis based on the results obtained during laboratory tests. Diagnosis should be approached comprehensively, so the patient may be prescribed referrals for instrumental procedures.
The clinician needs:
- get acquainted with medical histories;
- collect and study a life history to determine the mechanism of infection;
- examine and carefully palpate the external male genitalia;
- perform a digital rectal examination;
- interview the patient in detail - clarify when the first signs of gonorrhea in men appeared, and determine the degree of their severity.
Basic laboratory tests that help identify the pathogen and select a medicine for gonorrhea:
- general clinical blood and urine tests;
- blood biochemistry;
- spermogram;
- PCR tests;
- serological tests;
- bacterial culture and microscopic examination of the material - a smear for gonorrhea in men is taken from the urethra and oral cavity.
Thanks to the results of such a diagnostic course, a individual scheme therapy for gonorrhea.
In some cases, the following instrumental procedures are additionally indicated:
- ultrasonography of the pelvic organs;
- fluoroscopy;
- urethroscopy.

It is necessary to differentiate gonococcal infection in men from the following diseases:
- syphilis;
- chlamydia;
- trichomoniasis.
Treatment
You can get rid of gonorrhea using conservative therapeutic methods, including taking medications and physiotherapeutic procedures.
Most often, patients are prescribed the following pills for gonorrhea:
- antibiotics - taken in courses under strict control attending physician;
- probiotics and prebiotics - necessary to restore microflora;
- hepatoprotectors;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory substances;
- immunomodulators;
- vitamin complexes.
The most commonly prescribed drugs for gonorrhea for men are:
- medicines of the penicillin group;
- "Ecmonovocillin";
- "Ceftazidime";
- "Phenoxymethylpenicillin";
- "Streptomycin";
- "Bicillin";
- "Kanamycin";
- "Ofloxacin";
- "Norsulfazole";
- "Ceftriaxone".
The list of how gonorrhea in men is treated with physiotherapy includes the following procedures:
- electrophoresis;
- UFO and UHF;
- magnetic therapy;
- laser therapy;
- autohemotherapy.
It is very important that both sexual partners undergo the appropriate course of treatment.
It is worth noting that treatment of gonorrhea in men at home by using folk remedies It is not advisable to carry out, since it can cause negative consequences.
Possible complications
Consequences of gonorrhea in men:
- balanitis and;
Negative consequences develop against the background of inadequate or independent treatment of the acute form of infection and if treatment for chronic gonorrhea in men is completely absent.
Prevention and prognosis
To avoid problems with infection and treatment of gonorrhea, the following general preventive recommendations must be followed:
- complete exclusion of casual sexual relations;
- using contraceptives during sex;
- compliance with the rules of intimate hygiene;
- early detection and elimination of STDs;
- strengthening the immune system - you should constantly take appropriate medications;
- regular, at least 2 times a year, visits to the urologist.
Early noted symptoms and treatment, wisely chosen by the doctor, are the main factors that dictate the prognosis of gonococcal infection. Ignoring clinical signs and refusing qualified assistance inevitably leads to complications.

Gonorrhea, or otherwise the gonorrhea, is one of the most common sexually transmitted infectious diseases worldwide. Literally the name gonorrhea means “seminal fluid”, and the colloquial designation “gonorrhea” comes from the second half of the 17th century from German word“drippen” (drips). Both names indicate the main symptom of gonorrhea in men and women - discharge from the genitals.
The main cause of gonorrhea is the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae, which was discovered in 1879 by Albert Neisser.
Gonorrhea affects warm, moist areas of the body, including:
- urethra (tube that drains urine from the bladder)
- eyes
- throat
- vagina
- female reproductive tract (fallopian tubes, cervix and uterus)
Gonorrhea is a highly contagious disease; according to the World Health Organization, 106 million new cases of the disease are registered annually worldwide and it ranks third among sexually transmitted infections. The pathogen affects both men and women, and in unfavorable cases, newborn children. It occurs mainly in young people 15-25 years old, but can also occur in very young children and in older people.
Gonorrhea is spread from person to person through unprotected oral, anal or vaginal sex. People with multiple sexual partners or those who do not use a condom are at greatest risk of infection.
Before describing the first signs of gonorrhea, let's talk a little about this disease and why it is so important to catch even the first signs of the disease.
How is gonorrhea transmitted?
As we noted above, the main cause of the disease is the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae, otherwise called gonococcus, which is found only in humans.
In 99% of cases, the disease is transmitted sexually through direct contact of the gonococcus with the mucous membrane, for example, during unprotected sexual intercourse, as well as during anal or oral sex. Therefore, gonorrhea is classified as a sexually transmitted disease.
Women have a higher risk of infection (50-80%) than men (30-40%). This is explained by the anatomical features of men in the form of a long and narrow urethra, and therefore the gonococcus can be washed away in the urine.
There may also be an ascending route of transmission of the disease from pregnant mother to child. If the integrity of the membranes is preserved, the child is protected from the causative agent of the disease, but if they are damaged, the risk of bacteria entering the child increases. In addition, the disease can be transmitted to him when passing through the birth canal.
There is also a known contact route of transmission of gonorrhea through household items or personal hygiene items, mainly in girls (towel, bed or underwear, washcloth, co-sleeping with a person with gonorrhea). It comes into contact with the eyes when touched with contaminated hands. This route of transmission is rare because external environment gonococcus is extremely nonviable.
What happens when you become infected with gonorrhea?
When gonococcus enters the body, it attaches to the cells of the mucous membranes with the help of pili - special thread-like processes consisting of proteins. Having attached, it penetrates into the cell with the development of a purulent inflammatory reaction, first locally at the site of infection, subsequently spreading to neighboring tissues.
Approximately 5% of people who become ill have no initial signs of the disease, which is called the asymptomatic form, but they can still infect other people.
What are the first symptoms of gonorrhea you notice?
The first suspicions usually appear within 2-14 days after infection. However, some people infected with gonorrhea do not experience noticeable symptoms. It's important to remember that a person with gonorrhea who is not suspected of having the disease, also called an asymptomatic carrier, is still contagious. He is likely to pass the infection on to other partners, even if nothing bothers him yet.
Very often, the infection does not always cause clearly expressed signs of gonorrhea: discomfort is often absent, especially in women.
If complaints appear, they concern mainly the genital organs with typical general signs of the disease - unpleasant discharge and painful urination.
Despite this, the disease most often occurs differently in men and women, as well as in newborns.
In addition, gonorrhea can be acute or chronic. The acute form of the disease is characterized by correspondingly pronounced manifestations, while in the chronic form, external signals of the disease are weakly expressed or completely absent. The chronic form occurs mainly in women. In this case, the disease often manifests itself only as slight redness in the affected area. Therefore, the risk of infecting a sexual partner is very high in this case.
The first symptoms of gonorrhea in men
- -redness and swelling in the area of the mouth of the urethra is the first sign of the disease with a burning sensation when urinating. Mucous or mucopurulent discharge of a yellowish-cream color appears.
- if contact occurred anally, there will be redness and burning of the anal area, painful sensations during bowel movements, and unpleasant discharge.
- - if left untreated, after 2-3 weeks the process can cause pain in the prostate area, which indicates its involvement in the inflammatory process.
- -redness of the testicles and their appendages, swelling, pain when pressed often accompanies the disease.
- -redness and painful swelling of the glans penis and foreskin.
- -increase in body temperature.
- constant sore throat

However, the infection does not always cause a reaction similar to the manifestations of gonorrhea: about 25% of men do not experience any of the discomfort described above at the onset of the disease. At the same time, delay in starting treatment may result in complications of the disease, for example, inability to fertilize.

The first symptoms of gonorrhea in women
Many women may not have obvious signs of gonorrhea. When women do experience the first hints of illness, they are usually mild or similar to other infections. If there is pain in the lower abdomen, it is most likely very mild. This makes it difficult to correctly identify the disease. Gonorrheal infections may look like regular vaginal yeast or bacterial infections.
Symptoms of gonorrhea may be completely absent or may be so mild that they are ignored. In this case, the disease can even become chronic.
During sexual transmission, an inflammatory process develops first on the mucous membranes of the vagina and cervix, which is accompanied by unpleasant purulent discharge from the vagina of a yellowish-cream color.
In the absence of timely treatment, the process moves to the cervical canal and the mucous membrane of the uterus (endometrium) with the development of an inflammatory process in them, which is characterized by excessively long menstruation (menorrhagia) and bleeding between them.

With further progression of the disease, the inflammatory process may involve the fallopian tubes and ovaries, and due to the connection of the fallopian tubes with the abdominal cavity, inflammation of the peritoneum covering the pelvic organs (pelvioperitonitis) develops.
In most cases the most a clear sign The onset of gonorrhea in women, which should make you wary, is inflammation of the urethra and bladder, which is accompanied by painful urination and frequent urge to urinate.
With oral transmission, you should be alerted to inflammation and sore throat. But nevertheless, in 90% of cases these phenomena may be absent.
In the rectum, the process can develop through the anal method of infection or secondarily, passing from the genital organs to it due to its close anatomical location. It manifests itself as inflammation of the rectum, mucopurulent discharge and painful defecation.
Another sign is an increase in body temperature and pain in the lower abdomen.
Signs of gonorrhea in newborns
Gonococcal infection during pregnancy can lead to serious complications. In the first trimester of pregnancy, inflammation of the genital organs and peritoneum leads to fetal loss; in the second and third trimesters, ascending infections to the fetus are rare, since cervical mucus closes the uterus. If a pregnant woman transmits gonococcus to her child or as a result of premature discharge amniotic fluid or during childbirth, he develops manifestations of the disease that are not typical for gonorrhea.
Gonoblenorrhea is the most common symptom of gonorrhea in newborns. In other words, this is inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eyes (conjunctivitis) due to their contact with a pathogen from the uterine secretion. It manifests itself as swelling of the eyelids, redness of the conjunctiva and purulent discharge from the eyes. The consequence of this may be subsequent blindness in the child, so to avoid this, preventive measures are taken immediately after birth, which consists of using eye drops with an antibacterial effect.
Other, more rare manifestations in newborns manifest themselves in the form of inflammation of the mucous membranes in the nose, vagina and anus, or the disease is completely asymptomatic.
Common symptoms of gonorrhea in men and women
In both sexes, the infection can spread throughout the body and signs of the disease can occur in other places and organs.
Skin changes in the form of bleeding pustules throughout the body.
Eye damage in adults as a result of ingestion of gonococcus from the hands with the development of conjunctivitis. It is manifested by swollen eyelids, redness of the mucous membranes and purulent discharge from them.
Purulent, painful inflammation of the joints and ligaments, often affecting several joints (polyarthritis).
Inflammation of the soft meninges (meningitis) and the inner lining of the heart (endocarditis) are quite rare if the disease is not diagnosed in a timely manner and there is no treatment.
Without timely treatment, the disease often becomes chronic. In this case, local, pronounced signs of the disease disappear, but the causative agent of the disease penetrates into the deeper layers of tissue, where it causes chronic inflammation.
In men, this manifests itself in the form of chronic prostatitis or epididymitis (inflammation of the epididymis). In this case, purulent discharge is insignificant. Only at night does a purulent drop form, which always flows out of the urethra before the first morning urination (“visiting drop”).
In women, this is manifested by chronic inflammatory processes in the fallopian tubes (salpingitis) and ovaries (adnexitis), which can cause infertility. Complaints intensify during menstruation.
As a rule, the chronic form of the disease is difficult to treat, so do not delay going to the doctor!

How to identify gonorrhea in time?
As we said earlier, gonorrhea is a highly contagious disease, the timely detection of which and initiation of treatment will help to avoid further development complications. It is very important to identify gonorrhea in a timely manner. We have already talked about the first signs of gonorrhea, but in order to finally verify the presence of the disease, more subtle research methods are needed.
How is gonorrhea defined?
Like any other disease, gonorrhea is first determined by the simplest, and then by more complex methods:
1.Patient interview: the doctor finds out the patient’s complaints, when they first appeared, the method of infection, what medications were taken, whether there are other diseases, the presence of allergic reactions.
2.Patient examination: the doctor examines the affected area, checking for purulent discharge.
3.Laboratory tests to determine gonorrhea:
Microscopic method - the causative agent is detected in the resulting secretion under a microscope using special Gram or methylene blue staining. It is characterized by a typical bean-shaped shape and pairing, as well as an intracellular location. The reliability of this method is 50% when examining cervical mucus, cervical canal secretions, discharge from the anus and larynx, and asymptomatic cases. In men, examination of discharge from the urethra in the acute period, the reliability of this method is 90-100%.
Bacteriological culture of the secretion on a nutrient medium in order to obtain a growing colony of gonococcus, which will confirm the diagnosis. Also, an antibiogram is performed on the resulting bacterial culture in order to determine the sensitivity of the bacteria to them and, therefore, select the correct treatment. By the way, over the past few years, gonococcus resistance to antibiotics has been increasing.
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is based on the determination of antibodies in the patient’s blood to gonococcus.
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method is based on the determination of DNA characteristic of gonococcus. It is the most accurate diagnostic method than bacterial cultures.
Testing for sexually transmitted infections (STIs) is often recommended, since gonorrhea often occurs mixed with other infectious diseases of the genital organs. As a rule, tests are carried out for syphilis, HIV, hepatitis C, ureaplasmosis, chlamydia, etc.
Culture from the cervical canal for atypical cells in women.
General blood test: there is an increase in the level of leukocytes and rods, ESR.
General analysis of urine: its color is often cloudy due to purulent contents, especially in men, an increase in leukocytes, red blood cells and cylinders when the urinary system is involved in the process.
Biochemical blood test: in general, no changes. In acute cases, an increase in the acute phase marker of inflammation, C-reactive protein, may be observed.
4.Instrumental methods of determination:
Ultrasound of the pelvic organs to determine the extent of gonorrhea and the presence of other diseases.
If necessary, cystoscopy is performed to determine the condition of the bladder, and colposcopy to exclude malignant disease of the cervix in women.
All examinations are carried out before the start of treatment for the disease and 1-2 weeks after.
Treatment of gonorrhea - with what and how?
It goes without saying that treatment for gonorrhea should be carried out only after prescriptions made by the doctor, as well as together with all sexual partners who have had sexual contact with the sick patient.
Self-treatment is unacceptable, as it risks making the disease chronic and causing serious complications.
All treatment of gonorrhea consists of prescribing antibiotics, taking into account the obtained antibiogram. Antibacterial drugs were first used back in 1897 in the form of protargol, since 1935 treatment was carried out with sulfamides, and since 1944 the era of penicillin began.
But due to the increasing development of resistance to penicillin, other antibiotics began to be used to treat gonorrhea and today the following are prescribed:
3rd generation cephalosporins: ceftriaxone, cefixime. Ceftriaxone is prescribed at a dosage of 250 mg intramuscularly once, cefixime 400 mg intramuscularly once. IN severe cases Ceftazidime is recommended intramuscularly at a dosage of 1-2 g 2 times a day.
Fluoroquinolones: ciprofloxacin tablets at a dosage of 0.25-0.5 g 2 times a day in uncomplicated cases, in severe cases - 0.75 mg 2 times a day. The course of treatment is 7-14 days. Ofloxacin in a dosage of 0.2 g 2 times a day, in severe cases, 0.3-0.4 g 2 times a day for 7-10 days.
Macrolides: its most effective representative in this case is azithromycin, which is prescribed in the form of tablets in a dosage of 1 g once (2 tablets of 500 mg each), in severe cases, prescribed 1 g once a day three times with an interval of 7 days: 1st day - 7th day - 14th day.
Tetracyclines: tetracycline is prescribed in tablet form at a dosage of 0.25 mg 4 times a day for 7-10 days. Since gonorrhea often occurs with chlamydial infection, it sometimes makes sense to prescribe doxycycline 100-200 mg per day for 10-14 days; for pure gonorrhea, the dose is 100 mg 2 times a day for 2-4 days.
As a rule, gonorrhea is not treated by prescribing one antibiotic, but at least 2 different drugs are used for this purpose. The most effective combination for uncomplicated gonorrhea is azithromycin with ceftriaxone or doxycycline/tetracycline with ceftriaxone. For concomitant chlamydial infection, ceftriaxone is prescribed with doxycycline, since the latter is most active against chlamydia and gonococcus.
In severe cases of gonorrhea, the same antibiotics are prescribed, but the treatment period is longer - up to one month. For newborn children, antibiotics are prescribed in intramuscular or intravenous form, with additional eye rinsing with saline solution and instillation of drops with an antibacterial effect. Today, thanks to preventive measures, it is possible to avoid the development of gonorrhea in newborns from infected mothers.
In combination with an antibacterial agent, it is also recommended local treatment, which consists of washing the vagina, urethra, rectum with a solution of chamomile, 1-2% solution of protargol. Outside the period of exacerbation, physical treatment may be prescribed - ultraviolet irradiation of blood, electrophoresis, laser therapy.
In most cases, the gonococcus dies after starting to take antibiotics, but, nevertheless, it is not recommended to stop taking them, since ending treatment too early can cause a chronic form of this disease.
As we wrote earlier, all sexual partners with whom there was contact within 2 weeks before the appearance of signs of the disease are subject to treatment. After all, the possibility of infecting a partner exists even before any symptoms appear. If gonorrhea is asymptomatic, then all sexual partners with whom there was contact within 90 days are subject to treatment.
As a rule, the course of treatment for gonorrhea in an uncomplicated form is 7-14 days. A successful result is the disappearance of symptoms of the disease and the absence of gonococcus in laboratory tests 7-10 days after the end of treatment for gonorrhea.
And of course, no sexual intercourse during treatment!
If left untreated, will there be complications of gonorrhea?
Like any other disease, the lack of timely treatment for gonorrhea can lead to a number of complications:
Infertility in men and women,
Inflammation of joints and ligaments (arthritis and synovitis),
Inflammation of the conjunctiva of the eyes,
Inflammation of the inner lining of the heart (endocarditis) and the outer lining of the heart (pericarditis),
Inflammation of the soft meninges (meningitis),
Pustular formations on the skin,
Gonoblenorrhea in newborns, which can lead to the formation of ulcers on the cornea and, in extreme cases, loss of vision.
How to prevent gonorrhea?
Like any other sexually transmitted disease, preventing gonorrhea is very simple; it is enough to follow a number of preventive measures, namely:
- -exclude promiscuity,
- use a condom during sexual intercourse,
- -observe the rules of personal hygiene,
- -women and girls should not be allowed to use other personal linen or towels.
Basically, with correctly selected and timely therapy, gonorrhea can be cured quite successfully. Therapy must be prescribed by a venereologist; under no circumstances is self-treatment allowed!
In contact with
This article describes everything about gonorrhea, its signs and treatment, complications and prevention. This disease is one of the most famous sexually transmitted infections. Symptoms are more severe in men than in women.
The second name of the disease is gonorrhoea. It is difficult to treat, since the causative agent of gonorrhea constantly mutates and also gradually gets used to different antibiotics. Because of this, therapy may take months.
Description of the disease
What is gonorrhea? These are gonococci. This was discovered at the end of the 19th century. German scientist. Gonococci affect the mucous membranes, heart and other organs. Infection of the baby can even occur during childbirth.
Gonococci have round shape and bumpy surface. They are often found in pairs. Stained gonococci are clearly visible under a microscope. How is gonorrhea transmitted? Mainly through sexual contact.
Bacteria are not resistant to the external environment; light, heat, and disinfection solutions are fatal to them. Some gonococci exhibit resistance to penicillin.
Important! In case of gonorrhea they are not activated protective properties immunity. The disease can appear multiple times in the same person.
The incubation period of gonorrhea is from 2 to 15 days. Bacteria reproduce by fission and can exist in the intercellular space, but do not penetrate epithelial cells. Bacteria are able to change their size and combine. The infection spreads very quickly.
Types of gonorrhea

There are two types of gonorrhea. The acute form is accompanied by the rapid appearance of pronounced symptoms. They do not go away, but get stronger over time. Bacteria can be destroyed in the first two hours after infection, then the infection begins to develop rapidly.
Very rarely, chronic gonorrhea manifests itself with pronounced symptoms. At times they disappear completely. Men decide that the disease has gone away on its own and are in no hurry to see a doctor. However, the disease progresses further, so chronic gonorrhea is the most dangerous. It can lead to serious consequences.
Causes of the disease
Trigger sickness in men occurs mainly due to unprotected sex. Gonococci are transmitted during sexual intercourse. This happens in 50 percent of cases. Less commonly, infection occurs during oral sex. In this case, erosions appear in the mouth and throat. After infection (during the birth of the baby) the mucous membrane of the child’s eyes appears, ulcers appear that go away with difficulty.
Comment! The disease cannot be transmitted through personal belongings, since gonococci do not live in the external environment.
However, there is still a chance, albeit negligible, that you can become infected through the toilet, swimming pools, cutlery and kisses. Gonorrhea can be transmitted through intimate toys or vibrators used by a sick person.
Gonorrhea symptoms
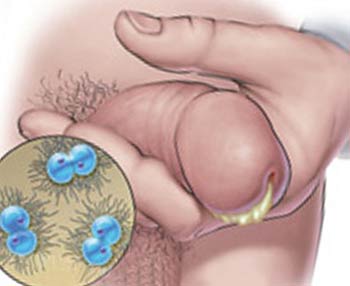
In the acute phase of gonorrhea, the first signs appear a couple of days after infection. Symptoms in men are more pronounced. The duration of this form of the disease varies. Most often, the acute phase lasts for two months.
Symptoms in acute form
Initial signs of gonorrhea in men:
- itching and burning begin in the urethra and intensify when urinating;
- when pressing on the penis, thick white purulent discharge flows out of it;
- redness of the head of the penis;
- there is a frequent urge to go to the toilet;
- swelling of the urethra appears;
- her holes stick together.
Initially, the discharge is not abundant, it has gray shade(they are in the photo). Gradually, the symptoms of the disease intensify. Abundant yellow-green mucus appears. When urinating, the pain intensifies significantly. An erection often occurs at night. It is accompanied by severe pain.
Symptoms in chronic form
With the chronic form of gonorrhea, the routes of infection become more and more extensive. The infection spreads to the testicles and prostate gland. The urge to urinate becomes more frequent, the erection is longer and more painful. In advanced cases, this sensation is observed in the intestines during bowel movements.
The groin area is affected. An inflammatory process begins in the testicles, which is accompanied by swelling of nearby tissues and lymph nodes. During sex, pain and bleeding occur.
Attention! Characteristic sign gonorrhea in the chronic form of a sexually transmitted disease - a small cloudy drop that appears in the morning in the opening of the urethra.
Symptoms of gonorrhea in men may be subtle or not appear for a long period. As a result, the patient does not begin treatment and the gonorrhea continues to progress. Its symptoms often appear only in the later stages, so there are additional serious consequences.
Complications of gonorrhea
Complications most often appear with the chronic form of gonorrhea. Such consequences result from the lack of treatment in the initial stages of the disease, which can be difficult to recognize. Because of this, the infection strikes internal organs, causes inflammation.
| Name of the disease | Symptoms |
| Gonorrheal | The main symptoms include erosions that appear on the head of the penis. In the acute phase, a urine sample can be taken when two containers are filled with it. In the first, when urination begins, the liquid will be cloudy, with pus, and the liquid collected at the end of the process will be clear. After a few days, the acute form becomes less pronounced. The color of the head of the penis becomes normal, pus appears on the panties only in the morning. When urinating, there is almost no pain when pressing. However, urine samples remain the same. |
| Attaching an additional infection to the gonorrhea. Inflammation of the head of the penis and foreskin occurs. This is accompanied by pain, itching and burning. During sex, discomfort is observed, dry skin appears, and erosion appears on the head of the penis. Gradually, the same lesions cover the foreskin. It shrinks greatly and scars appear on it. | |
| Cystitis | There is a frequent urge to go to the toilet. At the same time it is felt strong pain, urine with blood appears. |
| Cavernite | The inflammatory process begins in the cavernous thalamus of the penis. It begins to bend during an erection, and severe pain appears. |
| Colliculitis | Inflammation of the seminal tubercles. This is accompanied by frequent and painful erections and wet dreams. Blood appears in the seminal fluid. |
| Dereferentit | Purulent inflammatory process. He appears in the stream that carries the seed. The disease appears along with epididymitis. The spermatic cord becomes very dense and swells. |
| Orchitis | Inflammation of the testicles. There is constant pain in the scrotum, it becomes red and swollen. Body temperature rises to 40 degrees. Weakness appears, the man may lose consciousness. Orchitis is a consequence of an advanced form of gonorrhea. |
| Vesiculitis | Inflammation of the seminal vesicles. Accompanied by pain and burning in the urethra. A discharge appears from it. An erection and painful ejaculation often occur. Blood is found in the urine. |
| Gonorrheal proctitis | Its appearance is indicated by severe itching in the anus and pain during bowel movements. |
| Blennorea | Bactria that get on the mucous membrane of the eyes cause profuse purulent lacrimation. This can lead to vision loss. |
| Gonorrheal pharyngitis and tonsillitis | The diseases are asymptomatic. It just hurts for a man to swallow. |
Accompanied by a burning sensation in the perineum, pain during urination, frequent urge to urinate, with initial urinary retention. Purulent inflammation and enlargement of the prostate begin. The most common consequences of gonorrhea are epididymitis and prostatitis. In the chronic form of the disease, men experience infertility.
Treatment of gonorrhea

It is best to start symptoms and treatment of gonorrhea in men at an early stage. Therapy is aimed at exterminating gonococci. A dermatovenerologist treats gonorrhea. First, the causes of the disease are established. Then a treatment regimen is developed. Therapy takes a long time, as bacteria quickly become accustomed to antibiotics.


Because of this, drugs are prescribed only after the results of bacterioculture. The most commonly prescribed are Bicillin, Ceftriaxone and some other antibiotics. During treatment, two drugs are used simultaneously. Azithromycin is considered the best antibiotic for treating gonorrhea. The drug "Sumamed" is used if the sensitivity of gonococci to the group of macrolides is detected.


Additionally, microenemas with antibacterial solutions are given. To restore the strengthening of the immune system, vitamins () and restorative drugs are prescribed. Additionally, medications are used to maintain the functioning of the heart, kidneys, and liver.
During treatment for gonorrhea, the patient should drink a lot of water. Diuretics help flush out gonococci, pus, and infected areas of mucous membranes from the body. If there are additional diseases, then their treatment is carried out simultaneously.
After starting therapy, the patient undergoes repeated tests after 10-14 days.
Based on the results, treatment of gonorrhea in men is adjusted. Other medications may be prescribed or the dosage of previous medications may be changed. The following tests (smear, blood, urine) are taken only after 4 weeks. Even if gonorrhea is completely cured, a man should be examined every 6 months for two years.
Treating gonorrhea at home

Treatment of gonorrhea in a hospital is indicated only in case of relapse of the disease, complications or additional infection. In other cases, treatment is carried out at home. In addition to prescribed medications, folk recipes are also used.
To enhance treatment, infusions and douches of herbs are used. Effective assistance Chamomile helps in therapy. It has wound healing, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects. An infusion is made from chamomile, which is used for lotions and baths. The liquid is also poured into the urethra using a pipette.
How to treat gonorrhea with burdock? The roots of the plant are used for this. A decoction is made from them, which is similar in healing properties with chamomile infusion. Baths for the scrotum and penis are made from a product based on burdock roots.
It is used to enhance the functioning of the immune system. You need to drink it in the morning, before meals, 5 drops. Ginseng helps improve blood circulation and strengthens mucous membranes.
Many vegetables and fruits have an antibacterial effect. A man should eat parsley every day, berries(especially viburnum, blueberries and lingonberries). The listed recipes, herbs, vegetables and fruits help speed up recovery.
Watch the video - symptoms and treatment of gonorrhea:
Disease prevention

Infection with gonorrhea is most often possible through unprotected sex. To prevent infection, it is necessary to avoid promiscuity. Condoms must be used during sexual intercourse. If a man or his partner is sick, they should not have intimate relations until they are completely cured.
Personal hygiene must always be maintained. Prevention of gonorrhea involves antibacterial treatment of the genitals after unprotected sex. In this case, the man should immediately thoroughly wash the urethra and penis with soap. Then treat the genitals with a weak solution of potassium permanganate or Miramistin. This drug will reduce the risk of infection tenfold. It is easier to follow prevention recommendations than to treat gonorrhea.
Tripper is one of the most common sexually transmitted diseases in men. Launched form Gonorrhea is difficult to treat. The urethra most often suffers from gonococci. Bacteria are getting used to antibiotics more and more easily. As a result, treatment becomes even more complicated. Refusal of treatment or starting it in late stages can lead to infertility.
It should be borne in mind that in 25% of patients, gonorrhea is asymptomatic, as a result of which it goes unnoticed. According to statistics, for last years the number of cases of asymptomatic gonorrheal infection increased by 80%. Experts explain this fact by the fact that under the influence of antibacterial agents, which most modern people use quite often, the biological properties gonococci. Taking small doses of antibiotics can reduce the activity of gonococci, but will not cure the body of gonorrhea. A man with asymptomatic gonorrhoea remains contagious to sexual partners, and the disease gradually progresses, affecting his body.
The severity and nature of clinical manifestations of gonorrhea in men are individual and depend on the form, stage of the pathological process, localization and prevalence of infection, the presence of concomitant diseases and other factors.
For early diagnosis of pathology, in the article we will analyze how gonorrhea manifests itself in men and if any symptoms occur, consultation and examination by a venereologist is necessary.
Gonorrhea in men: first signs and symptoms
The symptoms and course of gonorrhea depend on the organ affected by the infection. The genitourinary organs are most vulnerable to gonococci (infection occurs through vaginal sexual intercourse). Therefore, the most common manifestation of gonorrhea is gonorrheal urethritis.
The first symptom of inflammation of the urethra is pain and burning in the urethra when urinating. After a few days, the signs of pathology intensify: purulent discharge begins to appear from the urethra. unpleasant smell the discharge is brownish-yellowish, the outer opening of the canal swells. Over time, the leucorrhoea becomes thicker and the urethral opening becomes red. Small ulcers may form on the urethra.
In men, discharge appears spontaneously or when pressure is applied to the penis. The urethral sponges begin to become inflamed and painful. If treatment is not resorted to, the infection spreads throughout the urethra, moving to the prostate, testicles, and seminal vesicles. Urination becomes difficult, frequent, or painful. Urine changes its color, consistency, and may contain blood, pus, or mucus. In some situations, there is pain during bowel movements or in the lower abdomen, fever, and chills.
Other signs of gonorrhea in men
If, after infection with gonococcus, the infection does not enter the genitals, but into the oral cavity (in this case, infection occurs through oral contact), gonorrheal pharyngitis or stomatitis occurs. In addition to women, the development of such diseases is typical for gay men (homosexuals).
Pharyngitis with gonorrhea is often asymptomatic. Patients often experience a sore throat, which can be severe or moderate, and excessive salivation. There may be difficulty swallowing, redness of the tonsils and pharynx, the appearance of a purulent-mucous coating on them, as well as swelling of the uvula and arches.
If gonorrhea infection occurs during anal intimacy, gonococci infect the rectum, provoking an inflammatory process - gonorrheal proctitis. Like gonorrheal pharyngitis, this form of gonorrhea occurs in bisexual and homosexual men.
Gonorrheal proctitis can occur without significant symptoms or manifest itself with discharge, pain and itching of the anus. In men, gonorrheal proctitis can develop into a severe form, which is accompanied by the formation of mucopurulent plaque on the walls of the rectum.
Chronic gonorrhea in men
In the absence of timely therapy or incorrectly developed therapeutic tactics, after 2-3 weeks the gonorrhea becomes chronic. This type of gonorrheal infection is characterized by the presence of a symptom called “morning drop syndrome.” Its essence lies in the fact that in the morning, after sleep, a drop of cloudy liquid containing pus appears at the opening of the urethra. When gonorrhea becomes chronic, acute pain disappears, urethral discharge stops or decreases, and the “morning drop syndrome” remains. There is also pain and burning when urinating.
Periods of remission and exacerbation in the chronic course of gonorrhea alternate. With each subsequent exacerbation, gonorrheal infection leads to the spread of inflammation and deeper disorders in the affected organs. Long-term gonorrhea can cause decreased libido, infertility and other sexual dysfunctions.
If the first signs of gonorrheal infection occur, contact a venereologist. Timely contact with a specialist and well-chosen therapeutic tactics will help diagnose the disease in the early stages, avoid the development of adverse consequences and completely get rid of the disease.
In order to understand how gonorrhea manifests itself in men, you need to have general idea about gonorrhea itself. Firstly, it is a sexually transmitted disease, the main route of transmission of which is sexual. Secondly, the infection affects the genitourinary system, causing inflammation and other symptoms characteristic of a particular disease. With this information, you can recognize the disease in time and consult a doctor.
In this article we will talk about the causes of the disease, find out how long it takes for gonorrhea to appear in men and what its characteristics, and also consider the most effective ways diagnostics
The causative agent of this sexually transmitted disease is gonococci - non-motile gram-negative paired cocci, shaped like coffee beans. Under unfavorable conditions, as well as when exposed to antibiotics, they are transformed into the L-form, or change their properties, turning into the Asha form.
In the host body, gonococci are highly sensitive, but outside of it they quickly die, for example, when the liquid in which they live dries out, as well as when heated to 40°C or higher. Death occurs almost instantly in soapy water, weak silver salts and antiseptic solutions.
Manifestations of gonorrhea in men appear after infection has occurred. The pathogen is mainly transmitted through sexual contact with an infected partner. This can be not only traditional sexual intercourse, but also anal or oral sex.
The contact and household route of infection is recorded much less frequently, due to the low resistance of gonococci in the external environment. With this method of infection, microbes enter the body of a healthy person after use. household items contaminated (bed linen, towels, washcloths, combs, etc.).

Duration of the incubation period and forms of gonorrhea
Once the gonococcus enters the mucous membrane, the countdown begins until the first symptoms appear. This period of time is called the incubation period. On average, the length of this period in men is about 15 days, but there may be changes both smaller and larger.
How quickly gonorrhea manifests itself in men depends on the following factors:
- characteristics of the pathogen;
- immune activity;
- the general health of the patient.




